C++ 核心编程 第一章 库是编程模块的集合,可以在程序中调用它们。库对很多常见的编程问题提供了可靠的解决方法,因此可以节省程序员大量的时间和工作量。
C++语言在c语言的基础上添加了面向对象编程 和泛型编程 的支持。c++继承了c语言高效,简洁,快速和可移植的传统。
C语言和C++并不是 对立的竞争关系。
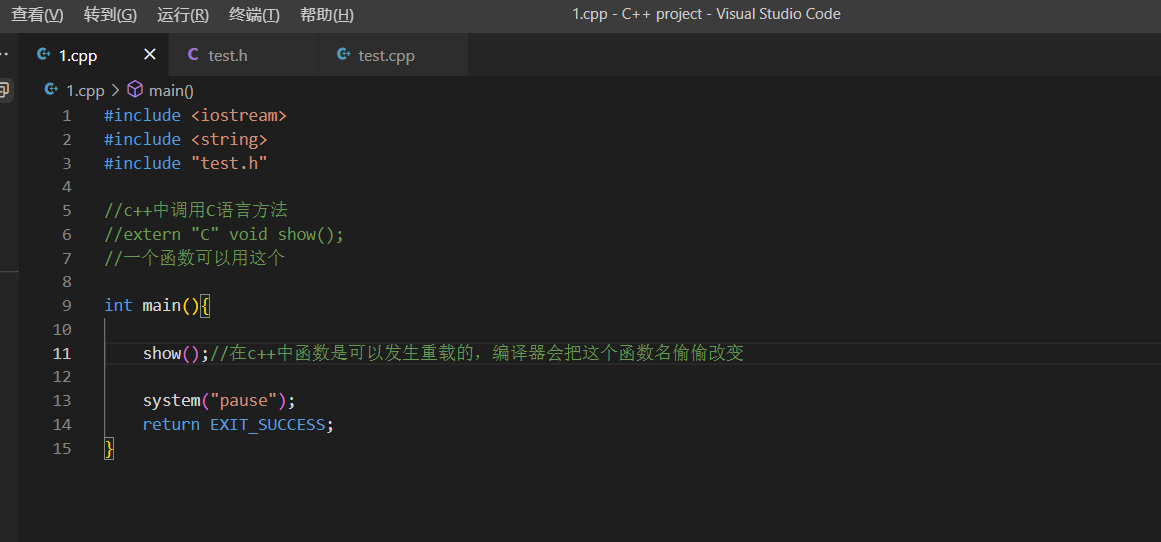
第二章 1.输出hello world 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> int main () std::cout<<"hello world!" <<std::endl; system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
using namespace std;是什么?
2.面向过程 面向过程是一种以过程为中心的编程思想。
通过分析出解决问题所需要的步骤,然后用函数把这些步骤一步一步实现,使用的时候—个一个依次调用就可以了。
面向过程编程思想的核心:功能分解,自顶向下-逐层细化(程序=数据结构+算法)。
面向过程编程语言存在的主要缺点是不符合人的思维习惯.而是要用计算机的思维方式去处理问题,而且面向过程编程语言重用性低,维护困难。
3.面向对象 面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming )简称OOP技术,是开发计算机应用程序的一种新方法、新思想。过去的面向过程编程常常会导致所有的代码都包含在几个模块中,使程序难以阅读和维护。在做一些修改时常常牵一动百,使以后的开发和维护难以为继。而使用OOP技术,常常要使用许多代码模块,每个模块都只提供特定的功能,它们
从上面的等式可以看出,程序就是许多对象在计算机中相继表现自己,而对象则是一个个程序实体。
4.面向对象的三大特性 封装,继承,多态。
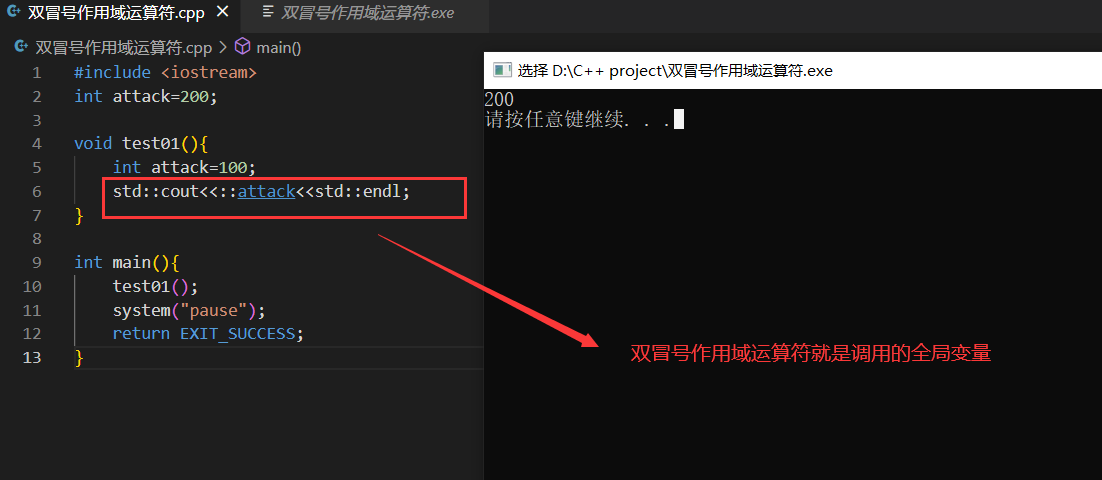
第三章 1.双冒号作用域运算符 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 #include <iostream> int attack=200 ;void test01 () int attack=100 ; std::cout<<attack<<std::endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
通常情况下,如果程序中既存在局部变量又存在全局变量,局部变量将会获得较高的优先权,它将屏蔽全局变量,但双冒号作用域运算符可以解决局部变量和全局变量重名的问题,当我们在变量前面加入::时,全局变量将获得较高的优先权。
插入一个问题与解决方式
只要将你命名的中文文件名换成英文的命名即可
2.namespace的使用 namespace命名空间主要用途用来解决命名冲突的问题
命名空间下可以存放 变量、函数、结构体、类…
命名空间只能存放在全局作用域下
命名空间可以嵌套命名空间
命名空间是开放的,可以随时添加新成员
命名空间是可以匿名的(?)
命名空间可以起别名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <iostream> namespace A{ int a=10 ; } namespace B{ int a=20 ; } int main () std::cout<<"A::a" <<A::a<<std::endl; std::cout<<"B::a" <<B::a<<std::endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <iostream> namespace A{ int a=10 ; namespace B{ int a=20 ; } } int main () std::cout<<"A::a" <<A::a<<std::endl; std::cout<<"A::B::a" <<A::B::a<<std::endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <iostream> namespace A{ int a=10 ; } namespace A{ void func () std::cout<<"hello namespace!" <<std::endl; } } int main () std::cout<<"A::a" <<A::a<<std::endl; A::func (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> namespace { int a=10 ; void func () std::cout<<"hello namespace!" <<std::endl; } } int main () std::cout<<"A::a" <<a<<std::endl; func (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <iostream> namespace A{ int a=10 ; } namespace A{ void func () std::cout<<"hello namespace!" <<std::endl; } } int main () namespace B=A; std::cout<<"A::a" <<A::a<<std::endl; A::func (); B::func (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
3.using的使用 我们可以通过using声明来指定特定命名空间的标识符
该代码会发生报错,因为写了using声明后,以后编译器默认sunwukongid是用 KingGlory下的,和编译器的局部变量就近原则产生了冲突,故程序会报错,在写代码时,我们要尽量避免二义性的发生。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 using namespace std;namespace zxy{ int a = 10 ; } void test01 () int a= 20 ; using namespace zxy; cout << a << endl; }
这样写将不会发生报错,using namespace zxy;只代表打开zxy这个房间,不对里面的标识符进行指定,编译器遵循就近原则。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 namespace A{ int paramA = 20 ; int paramB = 30 ; void funcA () "hello funcA" << endl; } void funcB () "hello funcB" << endl; } } void test01 () using namespace A; cout << paramA << endl; cout << paramB << endl; funcA (); funcB (); int paramA = 30 ; cout << paramA << endl; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 namespace B{ int paramA = 20 ; int paramB = 30 ; void funcA () "hello funcA" << endl; } void funcB () "hello funcB" << endl; } } void test02 () using namespace A; using namespace B; }
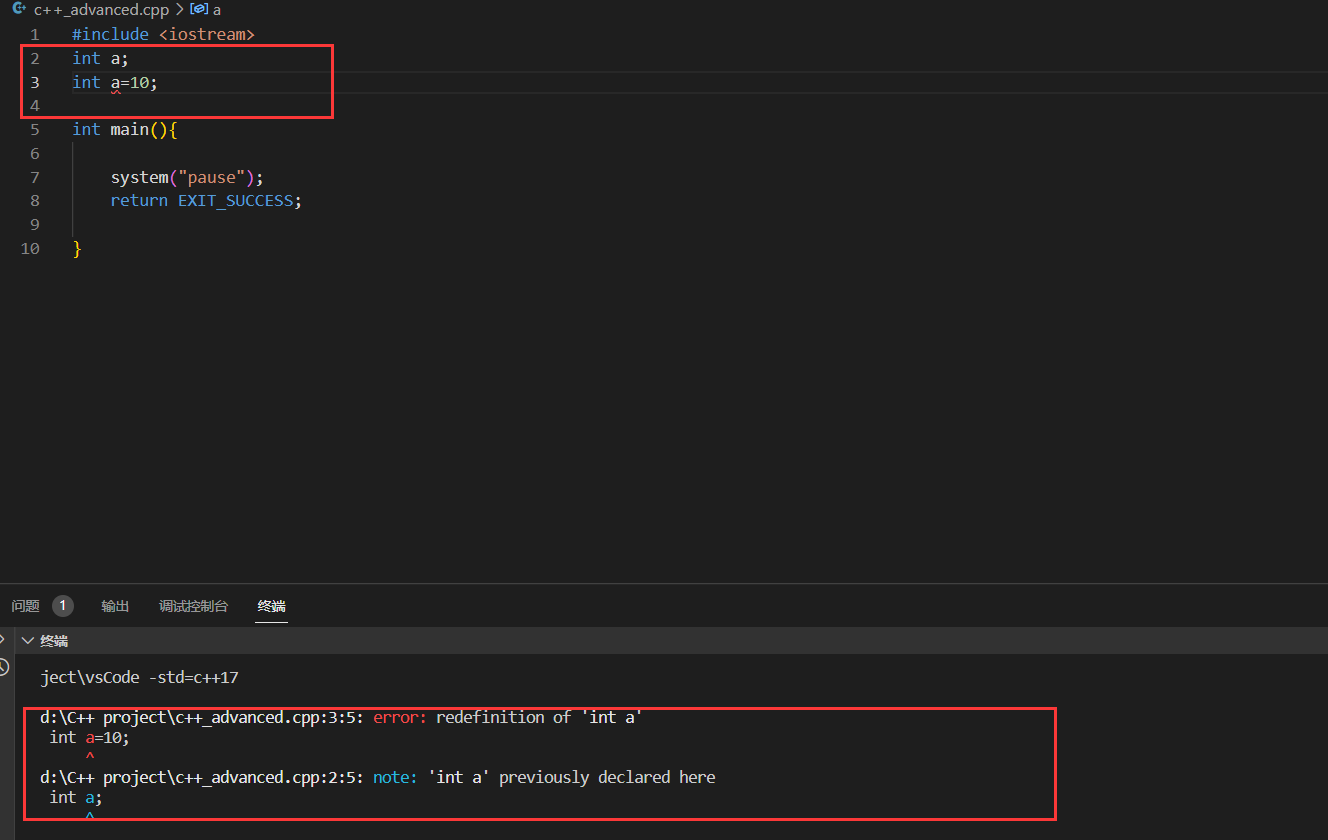
4.全局变量检测增强
在c语言中,前者这样的声明是可以被通过的。
5.函数检测增强
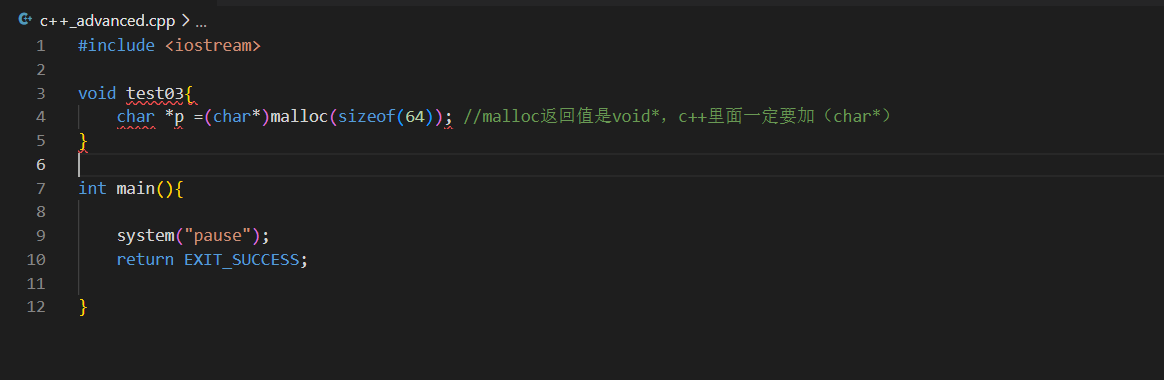
6.类型转化增强
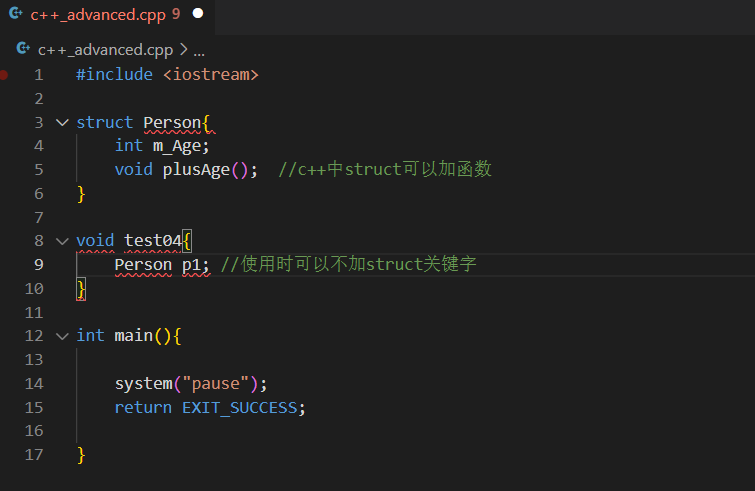
7.struct增强
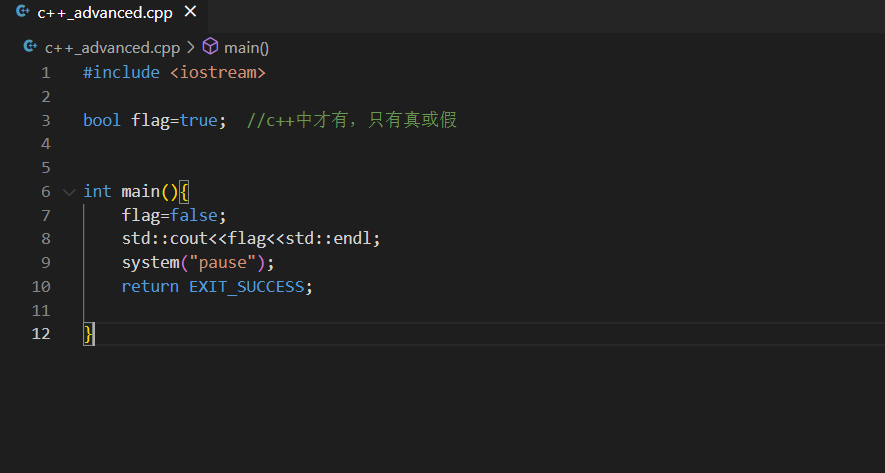
8.bool类型增强
C语言竟然是没有bool类型的。
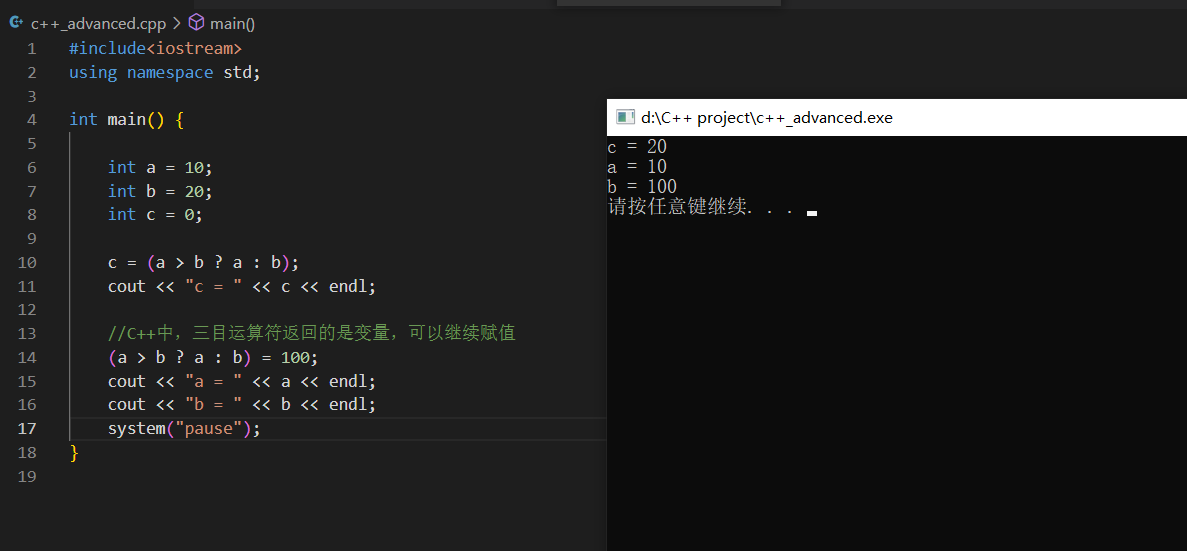
9.三目运算符增强
1 2 3 c=(a>b?a:b); 实际上等于 c=b;
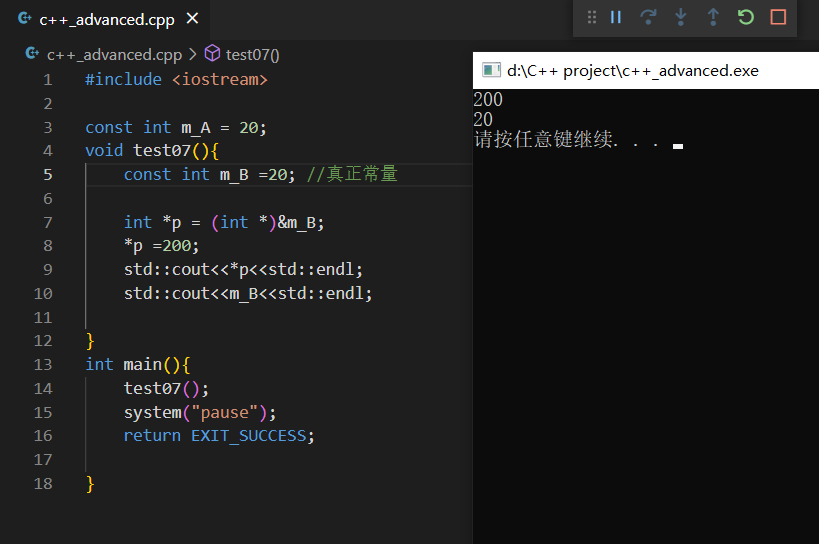
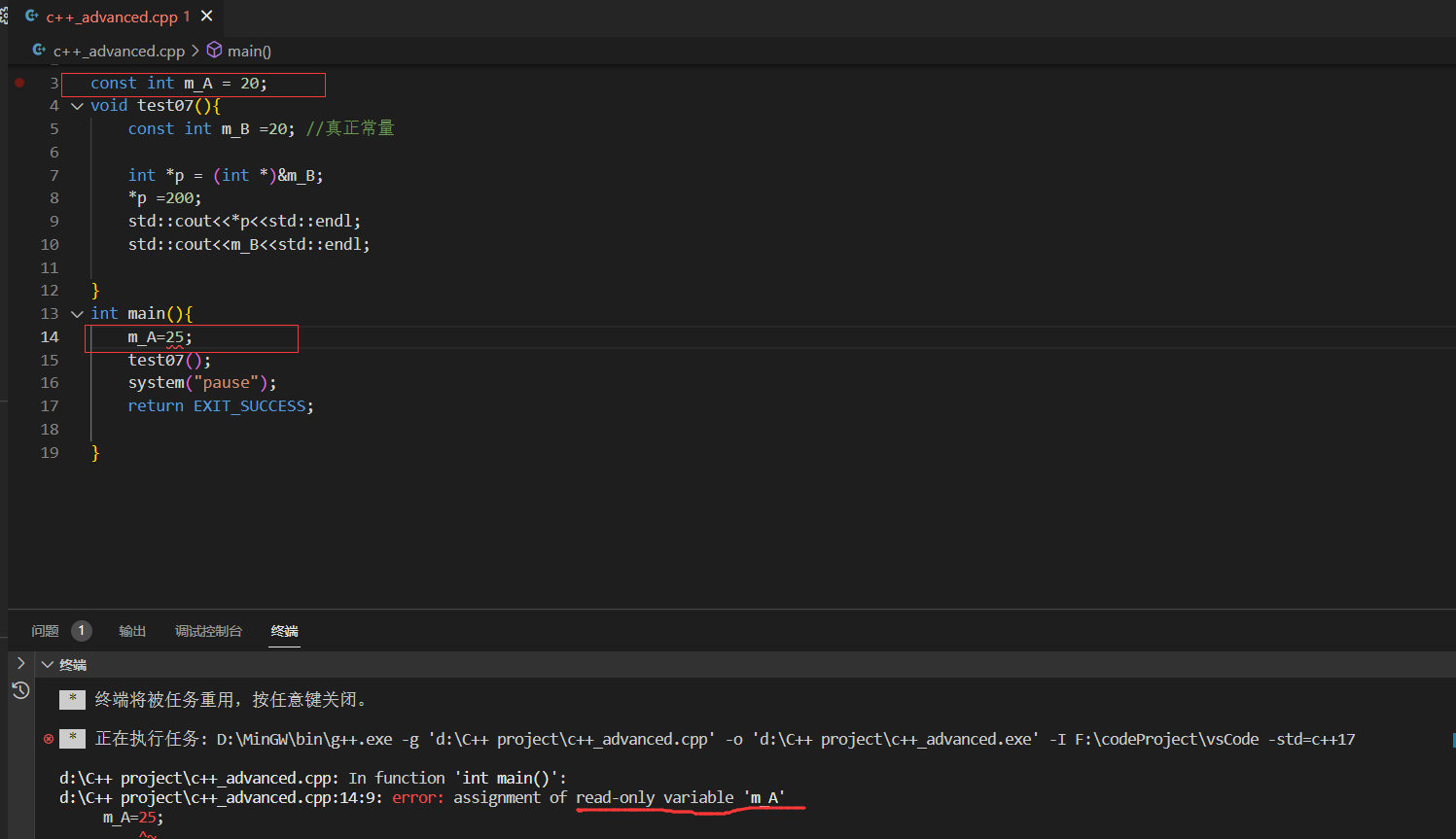
10.const增强
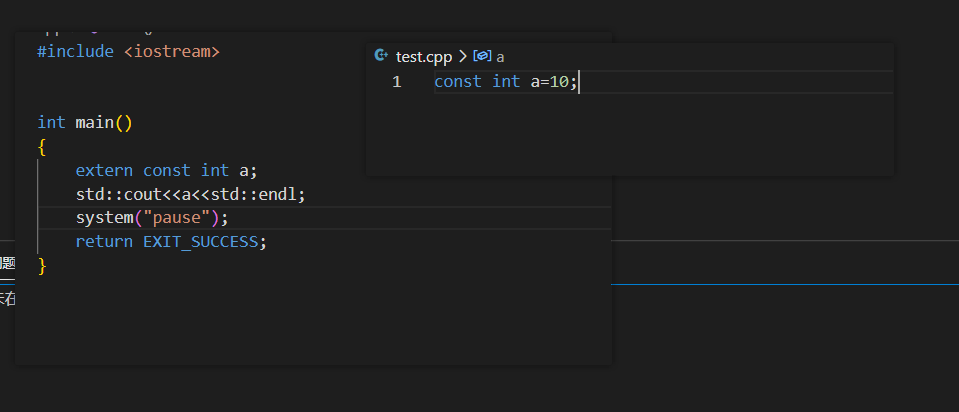
11.c++的const是内部链接
这样是没有a的值的。
要在test.cpp中加上extern const int a=10;
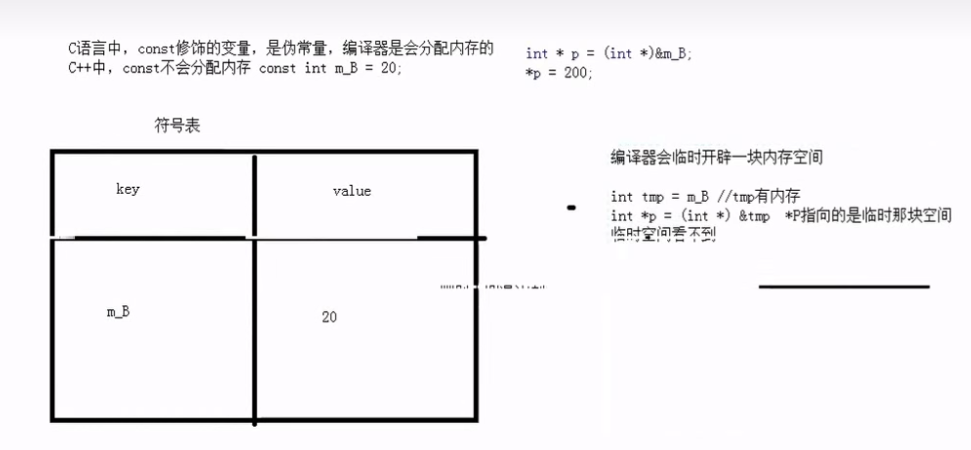
12.const分配内存的情况 1、对const变量取地址,会分配临时内存。(对临时内存的修改不影响符号表)
2、声明时加了extern,编译器也会分配内存(可通过地址修改值)
3、用普通变量初始化const变量,也会分配内存(可通过地址修改值)
4、自定义数据类型(struct)加const也会分配内存(可通过地址修改值)
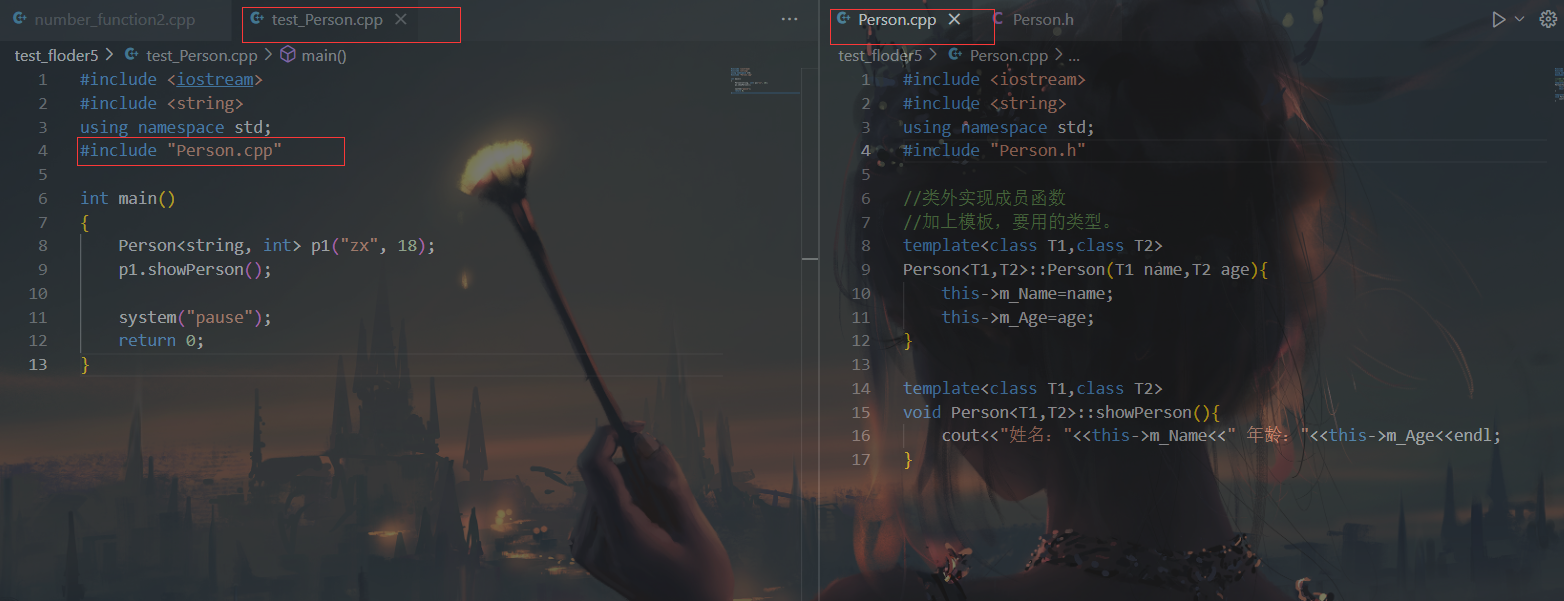
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () const int m_A = 10 ; int * p = (int *)&m_A; } void test02 () int a = 10 ; const int b = a; int * p = (int *) &b; *p = 1000 ; cout << "b = " << b << endl; } struct Person { string m_Name; int m_Age; }; void test03 () const Person p1={"zx" ,18 }; Person * p = (Person*)&p1; p->m_Name = "德玛西亚" ; (*p).m_Age = 18 ; cout << "姓名: " << p1.m_Name << " 年龄: " << p1.m_Age << endl; } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
13.尽量以const替换define
14.引用 1 引用的基本使用
作用 : 给变量起别名
语法: 数据类型 &别名 = 原名
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int main () int a = 10 ; int &b = a; cout << "a = " << a << endl; cout << "b = " << b << endl; b = 100 ; cout << "a = " << a << endl; cout << "b = " << b << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2 引用注意事项
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int main () int a = 10 ; int b = 20 ; int &c = a; c = b; cout << "a = " << a << endl; cout << "b = " << b << endl; cout << "c = " << c << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
3 引用做函数参数
作用:函数传参时,可以利用引用的技术让形参修饰实参
优点:可以简化指针修改实参
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 void mySwap01 (int a, int b) int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } void mySwap02 (int * a, int * b) int temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; } void mySwap03 (int & a, int & b) int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } int main () int a = 10 ; int b = 20 ; mySwap01 (a, b); cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; mySwap02 (&a, &b); cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; mySwap03 (a, b); cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
总结:通过引用参数产生的效果同按地址传递是一样的。引用的语法更清楚简单
4 引用做函数返回值
作用:引用是可以作为函数的返回值存在的
注意:不要返回局部变量引用
用法:函数调用作为左值
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 int & test01 () int a = 10 ; return a; } int & test02 () static int a = 20 ; return a; } int main () int & ref = test01 (); cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; int & ref2 = test02 (); cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; test02 () = 1000 ; cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
5 引用的本质
本质:引用的本质在c++内部实现是一个指针常量.
讲解示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void func (int & ref) ref = 100 ; } int main () int a = 10 ; int & ref = a; ref = 20 ; cout << "a:" << a << endl; cout << "ref:" << ref << endl; func (a); return 0 ; }
结论:C++推荐用引用技术,因为语法方便,引用本质是指针常量,但是所有的指针操作编译器都帮我们做了
6 常量引用
作用:常量引用主要用来修饰形参,防止误操作
在函数形参列表中,可以加const修饰形参,防止形参改变实参
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void showValue (const int & v) cout << v << endl; } int main () const int & ref = 10 ; cout << ref << endl; int a = 10 ; showValue (a); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
15.设计一个圆类,打印输出周长。 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <iostream> #include <string> const double pi=3.14 ; class Circle { public : int m_R; double caluclateZC () return 2 *pi*m_R; } void setR (int r) m_R=r; } }; void test01 () Circle c1; c1.m_R=10 ; c1.setR (12 ); std::cout<<"c1的周长为:" <<c1.caluclateZC ()<<std::endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
16.设计一个学生类,打印输出学号和姓名 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Student { public : std::string n_Name; int m_Id; void setName (std::string name) n_Name=name; } void setId (int id) m_Id=id; } void showInfo () std::cout<<"姓名:" <<n_Name<<" 学号:" <<m_Id<<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Student st; st.setName ("张三" ); st.setId (1 ); st.showInfo (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
类是对对象的抽象
对象是对类的实例
17.内联函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> #include <string> #define Myadd(x,y) ((x)+(y)) void test01 () int ret=Myadd (10 ,20 )*10 ; std::cout<<ret<<std::endl; } #define Mycompare(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b)) inline void mycompare (int a,int b) int ret=a<b?a:b; std::cout<<ret<<std::endl; } void test02 () int a=10 ; int b=20 ; mycompare (++a,b); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
内联函数的一些点:
18.占位参数和默认参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <string> void func (int a,int b=10 ,int c=1 ) std::cout<<"a+b+c:" <<a+b+c<<std::endl; } void test01 () func (1 ); func (1 ,2 ); func (1 ,2 ,3 ); } void func2 (int a,int ) } void test02 () func2 (2 ,1 ) } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
19.函数重载 19.1 函数重载概述 作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性
函数重载满足条件:
同一个作用域下
函数名称相同
函数参数类型不同 或者 个数不同 或者 顺序不同
注意: 函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 void func () cout << "func 的调用!" << endl; } void func (int a) cout << "func (int a) 的调用!" << endl; } void func (double a) cout << "func (double a)的调用!" << endl; } void func (int a ,double b) cout << "func (int a ,double b) 的调用!" << endl; } void func (double a ,int b) cout << "func (double a ,int b)的调用!" << endl; } int main () func (); func (10 ); func (3.14 ); func (10 ,3.14 ); func (3.14 ,10 ); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
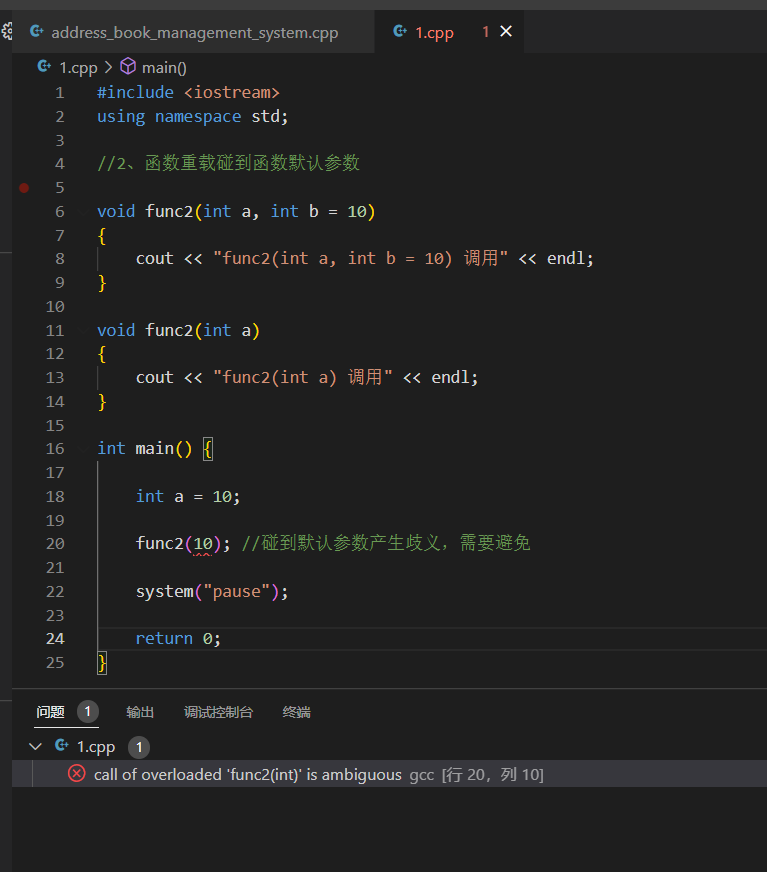
19.2 函数重载注意事项
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 void func (int &a) cout << "func (int &a) 调用 " << endl; } void func (const int &a) cout << "func (const int &a) 调用 " << endl; } void func2 (int a, int b = 10 ) cout << "func2(int a, int b = 10) 调用" << endl; } void func2 (int a) cout << "func2(int a) 调用" << endl; } int main () int a = 10 ; func (a); func (10 ); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
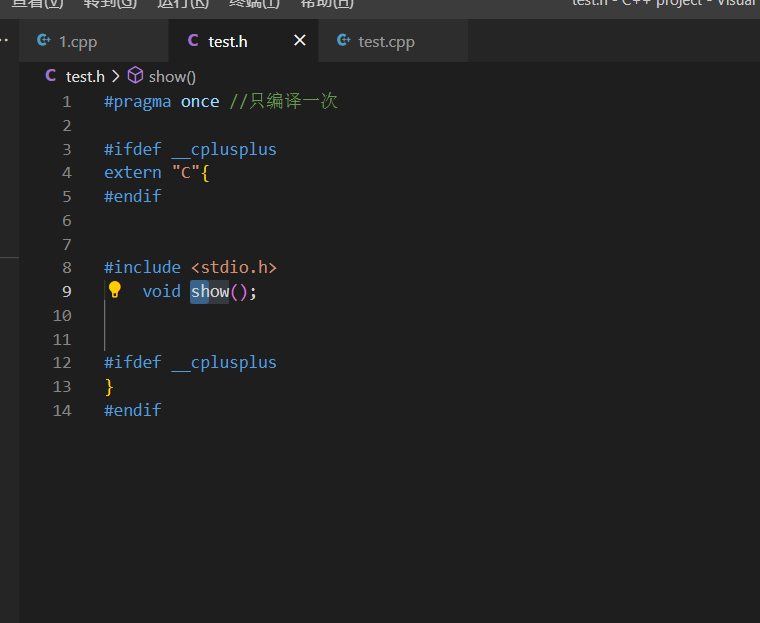
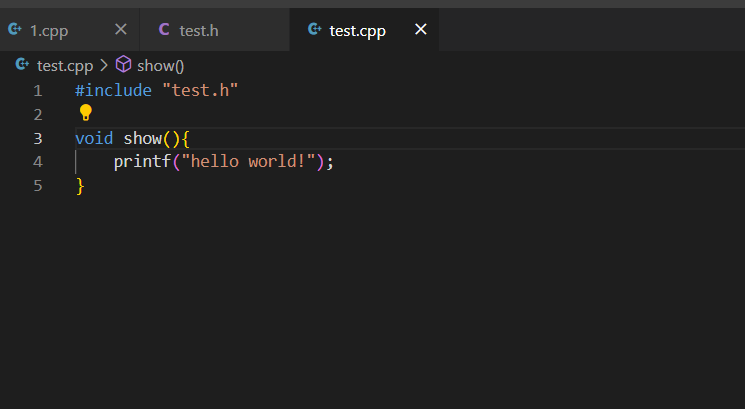
20.extern c浅析 在c++中调用C语言的代码。
21.C语言和c++的封装区别 封装的意义:
将属性和行为作为一个整体,用来表现生活中的事物
对函数和变量进行访问控制
C语言的封装:
C++语言的封装:
属性和行为绑定了,类型检测增强
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <iostream> #include <string> struct Person { char mName[64 ]; int mAge; void personeat () std::cout<<mName<<"在吃饭。" <<std::endl; } }; struct Dog { char mName[64 ]; int mAge; void dogeat () std::cout<<mName<<"在吃狗粮。" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person p1; strcpy (p1.mName,"老王" ); p1.personeat (); } int main () system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
22建议将成员变量都设置成私有 将成员变量设置为私有,外部不可访问,你可以在class中的public设置接口提供读写功能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Person { private : int m_Age=0 ; std::string m_Name; std::string m_lover; public : int getAge () return m_Age; } std::string getName () { return m_Name; } void setName (std::string name) m_Name=name; } void setLover (std::string lover) m_lover=lover; } }; void test01 () Person p1; std::cout<<"读取年龄" <<p1.getAge ()<<std::endl; p1.setName ("zx" ); std::cout<<"读取姓名" <<p1.getName ()<<std::endl; p1.setLover ("zwh" ); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
23.立方体案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <iostream> #include <String> class Cube { private : int m_L; int m_W; int m_H; public : void setL (int L) { m_L = L; } int getL () { return m_L; } void setW (int W) { m_W = W; } int getW () { return m_W; } void setH (int H) { m_H = H; } int getH () { return m_H; } void getCubeS () int s=2 *m_L*m_W+2 *m_W*m_H+2 *m_L*m_H; std::cout<<"立方体的面积是:" <<s<<std::endl; } void getCubeV () int v=m_H*m_L*m_W; std::cout<<"立方体的体积是:" <<v<<std::endl; } bool comparecube_class (Cube &cube) bool ret=m_L==cube.getL () &&m_H==cube.getH () &&m_W==cube.getW (); return ret; } }; bool compareCube (Cube &cube1,Cube &cube2) if (cube1.getL ()==cube2.getL () &&cube1.getH ()==cube2.getH () &&cube1.getW ()==cube2.getW ()){ return true ; } return false ; } void test01 () Cube c1; Cube c2; c1.setH (10 ); c1.setL (10 ); c1.setW (10 ); c1.getCubeS (); c1.getCubeV (); c2.setH (10 ); c2.setL (10 ); c2.setW (100 ); c2.getCubeS (); c2.getCubeV (); bool ret=compareCube (c1,c2); if (ret){ std::cout<<"c1和c2相等。" <<std::endl; } else { std::cout<<"c1和c2不相等。" <<std::endl; } } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
24.点和圆的关系 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Point { private : int p_x; int p_y; public : void setX (int x) p_x = x; } void setY (int y) p_y = y; } int showX () return p_x; } int showY () return p_y; } }; class Circle { private : Point center; int c_R; public : void setCenter (Point c) center = c; } void setR (int r) c_R = r; } Point showCenter () { return center; } int showR () return c_R; } }; void isInCircle (Circle &c , Point &p) int squareDistance = (c.showCenter ().showX () - p.showX ()) * (c.showCenter ().showX () - p.showX ()) + (c.showCenter ().showY () - p.showY ()) * (c.showCenter ().showY () - p.showY ()); int radius = c.showR (); if (squareDistance == radius * radius){ cout<<"点在圆上" <<endl; }else if (squareDistance < radius * radius){ cout<<"点在圆内" <<endl; } else if (squareDistance > radius * radius){ cout<<"点在圆外" <<endl; } } int main () Point cc; cc.setX (10 ); cc.setY (0 ); Circle c; c.setR (10 ); c.setCenter (cc); Point p; p.setX (10 ); p.setY (9 ); isInCircle (c,p); }
25.对象的构造和析构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <String> class Person { public : Person (){ std::cout<<"hello!" <<std::endl; } Person (int a){ std::cout<<"hello world!" <<std::endl; } ~Person (){ std::cout<<"hi!" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person p1 (2 ) ; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
解释 为什么Person p1;在主函数中,你只看到了构造函数?
c++析构函数的调用要在main()结束后(或者着说是main的最后语句执行完毕后)才调用的。其实在『请按任意键继续。。。。』后面还有析构调用的输出,只不过你没有看到。
注意:构造函数和析构函数在类中必须写在public下才可以调用到。
26.构造函数的分类和调用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <iostream> #include <String> class Person { public : int m_Age; Person (){ std::cout<<"无参构造函数" <<std::endl; } Person (int a){ std::cout<<"有参构造函数" <<std::endl; } Person (const Person& p){ m_Age=p.m_Age; std::cout<<"拷贝构造函数" <<std::endl; } ~Person (){ std::cout<<"析构函数" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person p1 (1 ) ; p1.m_Age=10 ; Person p2 (p1) ; std::cout<<"p2的年龄" <<p2.m_Age<<std::endl; Person p3; Person p4=Person (100 ); Person p5=Person (p4); Person p6=Person (); Person p7=100 ; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
27.拷贝函数的调用时机 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 #include <iostream> #include <String> class Person { public : int m_Age; Person (){ std::cout<<"无参构造函数" <<std::endl; } Person (int a){ std::cout<<"有参构造函数" <<std::endl; } Person (const Person& p){ m_Age=p.m_Age; std::cout<<"拷贝构造函数" <<std::endl; } ~Person (){ std::cout<<"析构函数" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person p1; p1.m_Age=10 ; Person p2 (p1) ; } void doWork (Person p1) } void test02 () Person p; p.m_Age=10 ; doWork (p); } Person doWork2 () { Person p1; return p1; } void test03 () Person p2=doWork2 (); } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
28.构造函数的调用规则 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <iostream> #include <string> class MyClass { public : MyClass (){ std::cout<<"默认构造函数" <<std::endl; } MyClass (int a){ std::cout<<"有参构造函数" <<std::endl; } MyClass (const MyClass& myclass){ std::cout<<"拷贝构造函数" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () MyClass c1; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
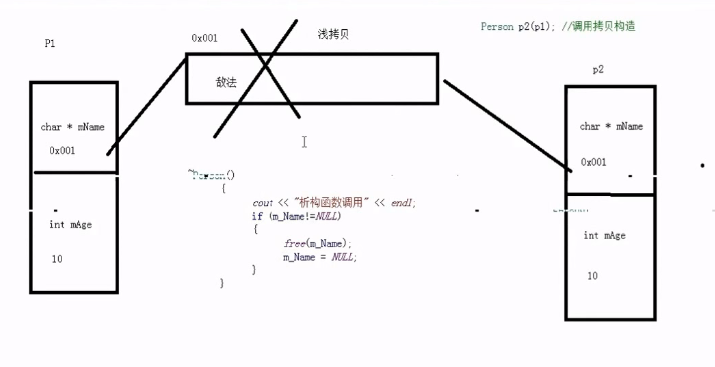
29.深拷贝和浅拷贝 我们首先要知道默认拷贝构造函数可以完成对象的数据成员简单的复制,这也称为浅拷贝 。对象的数据资源是由指针指向的堆时,默认的拷贝构造函数只是将指针复制 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Test { private : int * p; public : Test (int x) { this ->p=new int (x); cout << "对象被创建" << endl; } ~Test () { if (p != NULL ) { delete p; } cout << "对象被释放" << endl; } int getX () return *p; } }; int main () Test a (10 ) ; Test b = a; return 0 ; }
我们画一个示意图分析:
看懂了示意图,我们知道为什么会出错了(同一个内存被释放两次)。我们接下来分析解决方案:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Test { private : int * p; public : Test (int x) { this ->p=new int (x); cout << "对象被创建" << endl; } ~Test () { if (p != NULL ) { delete p; } cout << "对象被释放" << endl; } int getX () return *p; } Test (const Test& a) { this ->p = new int (*a.p); cout << "对象被创建" << endl; } }; int main () Test a (10 ) ; Test b = a; return 0 ; }
在未定义显示拷贝构造函数的情况下,系统会调用默认的拷贝函数——即浅拷贝,它能够完成成员的一一复制。当数据成员中没有指针时,浅拷贝是可行的;但当数据成员中有指针时,如果采用简单的浅拷贝,则两类中的两个指针将指向同一个地址,当对象快结束时,会调用两次析构函数,而导致指针悬挂现象,所以,此时,必须采用深拷贝。
深拷贝与浅拷贝的区别就在于深拷贝会在堆内存中另外申请空间来储存数据,从而也就解决了指针悬挂的问题。简而言之,当数据成员中有指针时,必须要用深拷贝。
30.初始化列表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Person { public : int m_A; int m_B; int m_C; Person (){} Person (int a,int b,int c):m_A (a),m_B (b),m_C (c) {} }; void test01 () Person p1 (10 ,20 ,30 ) ; std::cout<<"m_A:" <<p1.m_A<<std::endl; std::cout<<"m_B:" <<p1.m_B<<std::endl; std::cout<<"m_C:" <<p1.m_C<<std::endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
初始化列表建议用在有参构造函数中,一般语法就是:
类名(参数列表):类的成员属性(参数/值),...
{}
31.类对象作为类成员的案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Game { public : std::string m_GameName; Game (){ std::cout<<"game默认构造函数" <<std::endl; } Game (std::string name){ std::cout<<"game的有参构造函数" <<std::endl; m_GameName=name; } ~Game (){ std::cout<<"game析构函数" <<std::endl; } }; class Phone { public : std::string m_PhoneName; Phone (){ std::cout<<"phone默认构造函数" <<std::endl; } Phone (std::string name){ std::cout<<"phone的有参构造函数" <<std::endl; m_PhoneName=name; } ~Phone (){ std::cout<<"phone析构函数" <<std::endl; } }; class Person { public : std::string m_Name; Phone m_Phone; Game m_Game; Person (){ std::cout<<"person默认构造函数" <<std::endl; } Person (std::string name,std::string phoneName,std::string gameName):m_Name (name),m_Game (gameName),m_Phone (phoneName) { std::cout<<"person的有参构造函数" <<std::endl; } void playGame () std::cout<<m_Name<<"用" <<m_Phone.m_PhoneName<<"玩" <<m_Game.m_GameName<<std::endl; } ~Person (){ std::cout<<"person析构函数" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person p ("周幸" ,"平板" ,"PUBG" ) ; p.playGame (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
32.explict关键字作用 在C++中,explicit关键字用来修饰类的构造函数,被修饰的构造函数的类,不能发生相应的隐式类型转换,只能以显示的方式进行类型转换。
explicit使用注意事项:
explicit 关键字只能用于类内部的构造函数声明上。 explicit 关键字作用于单个参数的构造函数。 在C++中,explicit关键字用来修饰类的构造函数,被修饰的构造函数的类,不能发生相应的隐式类型转换。
在C++中,如果一个类有只有一个参数的构造函数,C++允许一种特殊的声明类变量的方式。在这种情况下,可以直接将一个对应于构造函数参数类型的数据直接赋值给类变量,编译器在编译时会自动进行类型转换,将对应于构造函数参数类型的数据转换为类的对象。如果在构造函数前加上explicit修饰词,则会禁止这种自动转换,在这种情况下,即使将对应于构造函数参数类型的数据直接赋值给类变量,编译器也会报错。下面以具体实例来说明。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class People { public : int age; People (int a) { age=a; } }; void test01 () People p1 (10 ) ; People p3=10 ; }
第一种是最一般的类变量声明方式。
explicit关键字到底是什么作用呢?它的作用就是禁止这个特性。
33.new运算符的使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Person { public : Person (){ std::cout<<"默认构造函数调用" <<std::endl; } ~Person (){ std::cout<<"析构函数调用" <<std::endl; } }; void test01 () Person *p2=new Person; delete p2; } void test02 () void *p=new Person; delete p; } void test03 () Person *pArray = new Person[10 ]; delete []pArray; } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
34.静态成员变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Person { public : static int m_Age; }; int Person::m_Age=0 ; void test01 () Person p1; p1.m_Age=10 ; Person p2; p2.m_Age=20 ; std::cout<<"P1:" <<p1.m_Age<<std::endl; std::cout<<"P2:" <<p2.m_Age<<std::endl; std::cout<<"通过类名访问age:" <<Person::m_Age<<std::endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
35.静态成员函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <iostream> #include <string> class Person { public : static int m_Age; static void func () std::cout<<"11" <<std::endl; } }; int Person::m_Age=0 ; void test01 () Person p1; p1.m_Age=10 ; Person p2; p2.m_Age=20 ; std::cout<<"P1:" <<p1.m_Age<<std::endl; std::cout<<"P2:" <<p2.m_Age<<std::endl; std::cout<<"通过类名访问age:" <<Person::m_Age<<std::endl; p1.func (); p2.func (); Person::func (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
36.单例模式的简介 单例模式(Singleton Pattern,也称为单件模式),使用最广泛的设计模式之一。其意图是保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点,该实例被所有程序模块共享。
37.单例模式案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <iostream> #include <string> class ChairMan { private : ChairMan (){ std::cout<<"创建国家主席类" <<std::endl; } ChairMan (const ChairMan& c){} static ChairMan * singleMan; public : static ChairMan* getInstance () return singleMan; } }; ChairMan * ChairMan::singleMan= new ChairMan; void test01 () ChairMan *cm1=ChairMan::getInstance (); ChairMan *cm2=ChairMan::getInstance (); if (cm1==cm2){ std::cout<<"cm1==cm2" <<std::endl; } else { std::cout<<"cm1!=cm2" <<std::endl; } ChairMan *cm3=new ChairMan (*cm2); if (cm3==cm2){ std::cout<<"cm3==cm2" <<std::endl; } else { std::cout<<"cm3!=cm2" <<std::endl; } } int main () std::cout<<"main调用" <<std::endl; test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Printer { private : Printer () { m_Count = 0 ; }; Printer (const Printer &p){}; static Printer *singlePrinter; int m_Count; public : static Printer *getInstance () { return singlePrinter; } void printText (string text) { cout << text << endl; m_Count++; cout << "打印机使用次数为: " << m_Count << endl; } }; Printer *Printer::singlePrinter = new Printer; void test1 () Printer *printer = Printer::getInstance (); printer->printText (" 报告1" ); printer->printText (" 报告2" ); printer->printText (" 报告3" ); Printer *printer2 = Printer::getInstance (); printer->printText (" 报告1" ); printer->printText (" 报告2" ); if (printer == printer2) { cout << "printer 等于 printer2 " << endl; } } int main () test1 (); Printer *printer = Printer::getInstance (); printer->printText (" 报告1" ); }
38.c++对象模型初探
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Person { public : int m_A; void func () static int m_B; static void func () }; void test01 () cout<<sizeof (Person)<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
39.this指针基本使用 如何区分p1和p2的func(),通过this指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Person { public : int age; Person (int age){ this ->age=age; }; void compareAge (Person &p) if (this ->age==p.age){ cout<<"年龄相等" <<endl; } else { cout<<"年龄不相等" <<endl; } }; Person& addAge (Person &p) { this ->age+=p.age; return *this ; } }; void test01 () Person p1 (10 ) ; cout<<"p1年龄:" <<p1.age<<endl; Person p2 (10 ) ; p1.compareAge (p2); p1.addAge (p2).addAge (p2); cout<<"p1年龄:" <<p1.age<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
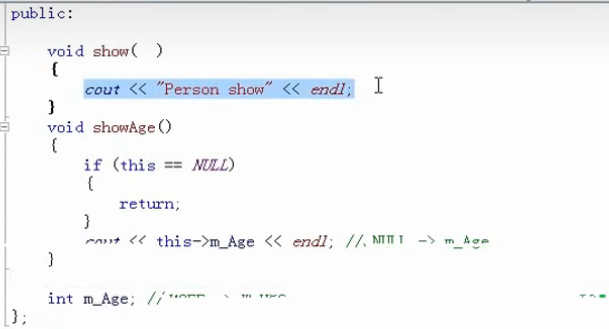
40.空指针访问成员函数 空指针可以访问成员函数(如果没有用到this->/*this)
如果用到了,那么建议判断(if(this==NULL))
41.常函数与常对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Person { public : int m_A; mutable int m_B; Person (){ this ->m_A=0 ; this ->m_B=0 ; } void showinfo () const this ->m_B=100 ; cout<<"m_A:" <<this ->m_A<<endl; cout<<"m_B:" <<this ->m_B<<endl; } }; void test01 () Person p1; p1.showinfo (); const Person p2; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
42.全局函数做友元函数 友元:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Building { friend void goodGay (Building *building) public : string m_SittingRoom; Building (){ this ->m_BedRoom="卧室" ; this ->m_SittingRoom="客厅" ; }; private : string m_BedRoom; }; void goodGay (Building *building) cout<<"好基友正在访问" <<building->m_SittingRoom<<endl; cout<<"好基友正在访问" <<building->m_BedRoom<<endl; } void test01 () Building *building=new Building; goodGay (building); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
43.整个类作为友元类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Building ;class goodfriend { public : goodfriend (); void visit () private : Building *building; }; class Building { friend class goodfriend ; public : string m_room; Building () { this ->m_Bedroom = "卧室" ; this ->m_room = "客厅" ; } private : string m_Bedroom; }; goodfriend::goodfriend () { building = new Building; } void goodfriend::visit () cout << "好朋友正在访问" << this ->building->m_room << endl; cout << "好朋友正在访问" << this ->building->m_Bedroom << endl; } void test () goodfriend gf; gf.visit (); } int main () test (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
让整个类作为友元类,是为了让这个类访问另一个类中的私有成员属性。
44.成员函数作为友元类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Building ;class goodfriend { public : goodfriend (); void visit () void visit2 () private : Building *building; }; class Building { friend void goodfriend::visit () public : string m_room; Building (){ this ->m_Bedroom="卧室" ; this ->m_room="客厅" ; } private : string m_Bedroom; }; goodfriend::goodfriend (){ building=new Building; } void goodfriend::visit () cout << "好朋友1正在访问" << this ->building->m_room << endl; cout << "好朋友1正在访问" << this ->building->m_Bedroom << endl; } void goodfriend::visit2 () cout << "好朋友2正在访问" << this ->building->m_room << endl; } void test () goodfriend gf; gf.visit (); gf.visit2 (); } int main () test (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
45.数组类的封装 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class MyArray { public : MyArray () { this ->m_Capacity = 100 ; this ->m_Size = 0 ; this ->pAddress = new int [this ->m_Capacity]; } MyArray (int capacity) { cout << "有参构造函数" << endl; this ->m_Capacity = capacity; this ->m_Size = 0 ; this ->pAddress = new int [this ->m_Capacity]; } MyArray (const MyArray &array) { cout << "拷贝构造函数" << endl; this ->pAddress = new int [array.m_Capacity]; this ->m_Size = array.m_Size; this ->m_Capacity = array.m_Capacity; for (int i = 0 ; i < array.m_Size; i++) { this ->pAddress[i] = array.pAddress[i]; } } ~MyArray () { cout << "析构函数" << endl; if (this ->pAddress != NULL ) { delete [] this ->pAddress; this ->pAddress = NULL ; } } void push_Back (int val) { this ->pAddress[this ->m_Size] = val; this ->m_Size++; } int getData (int index) { return this ->pAddress[index]; } void setData (int index, int val) { this ->pAddress[index] = val; } private : int *pAddress; int m_Size; int m_Capacity; }; void test01 () MyArray *array = new MyArray (30 ); MyArray *array2 = array; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { array2->push_Back (i); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { cout << array2->getData (i) << endl; } array2->setData (0 , 100 ); cout << array2->getData (0 ) << endl; delete array; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
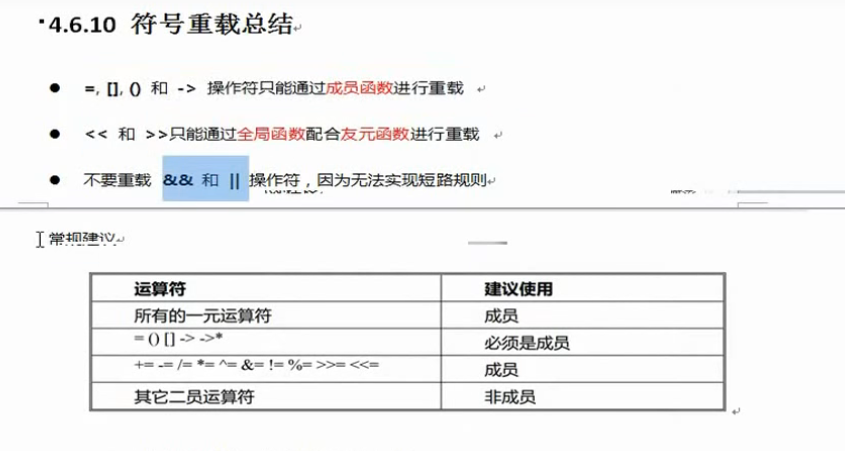
46.加号运算符重载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Person { public : int m_A; int m_B; Person (){}; Person (int a, int b) : m_A (a), m_B (b){}; }; Person operator +(Person &p1, Person &p2) { Person temp; temp.m_A = p1.m_A + p2.m_A; temp.m_B = p1.m_B + p2.m_B; return temp; } void test01 () Person p1 (10 , 10 ) ; Person p2 (10 , 15 ) ; Person p3 = p1 + p2; cout << "P3的m_A:" << p3.m_A << endl; cout << "P3的m_B:" << p3.m_B << endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
47.左移运算符重载 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Person { public : friend ostream& operator <<(ostream&cout ,const Person &p); Person (){}; Person (int a, int b){ this ->m_A=a; this ->m_B=b; }; private : int m_A; int m_B; }; ostream& operator <<(ostream&cout ,const Person &p){ cout<<"m_A=" <<p.m_A<<"m_B=" <<p.m_B; return cout; } void test01 () Person p1 (10 , 10 ) ; cout<<p1<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
48.前置后置运算符重载 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Complex { friend ostream &operator <<(ostream &out, const Complex &c); private : int m_a; int m_b; public : Complex (); Complex (int a, int b); Complex operator ++(int ); Complex &operator ++(); }; Complex::Complex () { } Complex::Complex (int a, int b) { m_a = a; m_b = b; } ostream &operator <<(ostream &out, const Complex &c) { out << c.m_a << " + " << c.m_b << "i" ; return out; } Complex Complex::operator ++(int ) { Complex tmp = *this ; this ->m_a++; this ->m_b++; return tmp; } Complex &Complex::operator ++() { this ->m_a++; this ->m_b++; return *this ; } int main () Complex c (1 , 2 ) ; cout << c++ << endl; cout << ++c << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
49.指针运算符重载(*) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Person { public : Person (int age){ this ->m_Age=age; } void showage () cout<<"年龄为:" <<this ->m_Age<<endl; } ~Person (){ cout<<"Person析构函数调用" <<endl; } int m_Age; }; class smartPointer { public : smartPointer (Person *person){ this ->person=person; } Person* operator ->(){ return this ->person; } Person& operator *(){ return *this ->person; } ~smartPointer (){ cout<<"智能指针析构了" <<endl; if (this ->person!=NULL ){ delete this ->person; this ->person=NULL ; } } private : Person *person; }; void test01 () smartPointer sp (new Person(10 )) ; sp->showage (); (*sp).showage (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
50.赋值运算符重载 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std;class Person { public : int m_A; Person (int a){ this ->m_A=a; } }; void test01 () Person p1 (10 ) ; Person p2 (0 ) ; cout<<"P2的m_A:" <<p2.m_A<<endl; p2=p1; cout<<"P2的m_A:" <<p2.m_A<<endl; } class Person2 { public : char *pName; Person2 (char *name){ this ->pName=new char [strlen (name)+1 ]; strcpy (this ->pName,name); } Person2& operator =(const Person2 &p){ if (this ->pName!=NULL ){ delete [] this ->pName; this ->pName=NULL ; } this ->pName= new char [strlen (p.pName)+1 ]; strcpy (this ->pName,p.pName); return *this ; } ~Person2 (){ if (this ->pName!=NULL ){ delete [] this ->pName; this ->pName=NULL ; } } }; void test02 () Person2 p1 ("狗蛋" ) ; Person2 p2 ("狗剩" ) ; p2=p1; cout<<p2.pName<<endl; Person2 p3 ("狗屁" ) ; p3=p2=p1; cout<<p3.pName<<endl; } void test03 () int a=10 ; int b=20 ; int c; c=a=b; cout<<a<<" " <<b<<" " <<c<<endl; } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
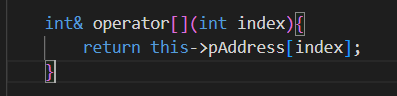
51.[]运算符重载
52.关系运算符重载 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 #include <iostream> using namespace std;#include <string> class Person { public : string p_name; int m_age; Person (string name, int age) { this ->m_age = age; this ->p_name = name; } bool operator ==(const Person &p) { if (this ->m_age == p.m_age && this ->p_name == p.p_name) { return true ; } return false ; } bool operator !=(const Person &p) { if (this ->m_age == p.m_age && this ->p_name == p.p_name) { return false ; } return true ; } }; void test01 () Person p1 ("周幸" ,18 ) ; Person p2 ("郑文慧" ,19 ) ; Person p3 ("郑文慧" ,19 ) ; if (p1 == p2) { cout << "p1和p2相等" << endl; } else { cout << "p1和p2不相等" << endl; } if (p3 == p2) { cout << "p3和p2相等" << endl; } else { cout << "p3和p2不相等" << endl; } if (p1 != p2) { cout << "p1和p2不相等" << endl; } else { cout << "p1和p2相等" << endl; } } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
53.函数调用运算符重载 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class Myprint { public : void operator () () cout<<"hello world" <<endl; } }; void test01 () Myprint myprint; myprint (); } class MyAdd { public : void operator () (int a,int b) cout<<"和为:" <<a+b<<endl; } }; void test02 () MyAdd myadd; myadd (1 ,2 ); MyAdd ()(1 ,3 ); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
54.字符串的封装(一) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <string.h> using namespace std;class Mystring { friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& cout, const Mystring &str); friend istream& operator >>(istream& cin, Mystring &str); public : Mystring (const char * str){ cout<<"有参构造调用" <<endl; this ->pstring= new char [strlen (str)+1 ]; strcpy (this ->pstring,str); this ->m_Size=strlen (str); } Mystring (const Mystring& str){ cout<<"拷贝构造调用" <<endl; this ->pstring= new char [strlen (str.pstring)+1 ]; strcpy (this ->pstring,str.pstring); this ->m_Size=str.m_Size; } ~Mystring (){ cout<<"析构调用" <<endl; if (this ->pstring!=NULL ){ delete [] this ->pstring; this ->pstring=NULL ; } } private : char *pstring; int m_Size; }; ostream& operator <<(ostream& cout, const Mystring &str){ cout<<str.pstring; return cout; } istream& operator >>(istream& cin, Mystring &str){ if (str.pstring!=NULL ){ delete [] str.pstring; str.pstring=NULL ; } char buf[1024 ]; cin>>buf; str.pstring=new char [strlen (buf)+1 ]; strcpy (str.pstring,buf); str.m_Size=strlen (buf); return cin; } void test01 () Mystring str="abc" ; cout<<str<<endl; cout<<"请输入新的字符串:" <<endl; cin>>str; cout<<str<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
不做二是因为差不多之前写过
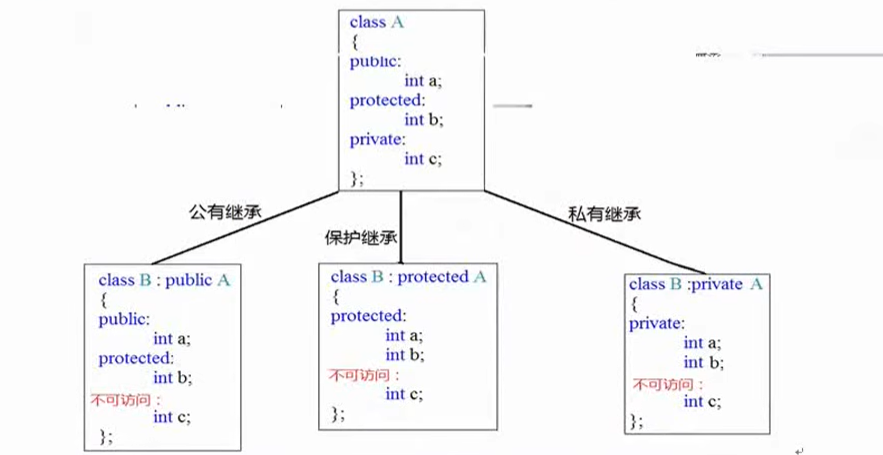
第四章 1.继承的引出,方式 继承可以减少代码的重复内容
基类(父类)
派生类(子类)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class CFather { public : int m_testA{0 }; protected : int m_testB{0 }; private : int m_testC{0 }; }; class CSon : public CFather{ void test () { m_testA = 1 ; m_testB = 1 ; m_testC = 1 ; } }; int main () CSon _test; _test.m_testA = 2 ; _test.m_testB = 2 ; _test.m_testC = 2 ; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class CFather { public : int m_testA{0 }; protected : int m_testB{0 }; private : int m_testC{0 }; }; class CSon : protected CFather{ void test () { m_testA = 1 ; m_testB = 1 ; m_testC = 1 ; } }; int main () CSon _test; _test.m_testA = 2 ; _test.m_testB = 2 ; _test.m_testC = 2 ; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class CFather { public : int m_testA{0 }; protected : int m_testB{0 }; private : int m_testC{0 }; }; class CSon : private CFather{ void test () { m_testA = 1 ; m_testB = 1 ; m_testC = 1 ; } }; int main () CSon _test; _test.m_testA = 2 ; _test.m_testB = 2 ; _test.m_testC = 2 ; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.继承中的对象模型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Base { public : int m_A; protected : int m_B; private : int m_C; }; class Son :public Base{ public : int m_D; }; void test01 () cout<<sizeof (Son)<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
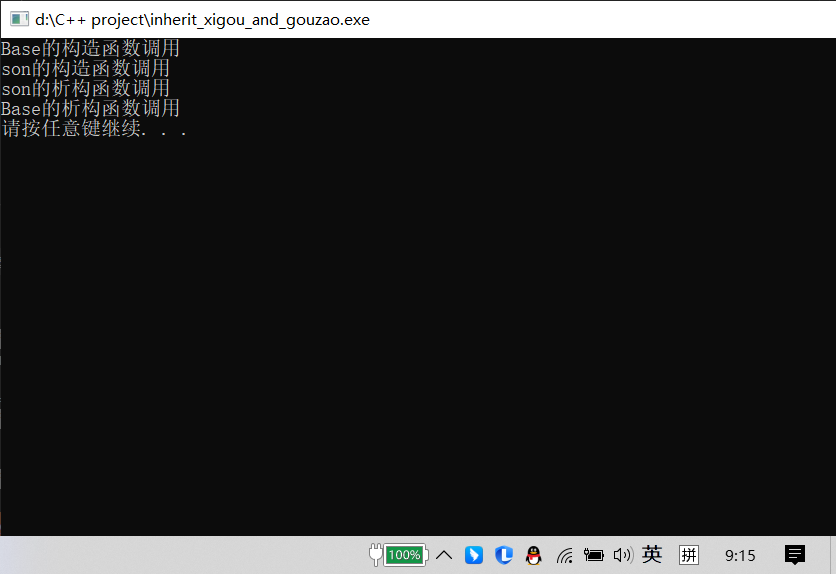
3.继承中的析构和构造 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Base { public : Base () { cout << "Base的构造函数调用" << endl; } ~Base () { cout << "Base的析构函数调用" << endl; } }; class Son :public Base{ public : Son (){ cout << "son的构造函数调用" << endl; } ~Son (){ cout << "son的析构函数调用" << endl; } }; void test01 () Son s1; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
如果父类中没有合适默认构造,那么子类可以利用初始化列表的方式显示的调用父类的其他构造。
operator=也不能被继承到子类
4.继承中的同名处理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Base { public : Base (){ m_A=100 ; } void func () cout<<"base的func调用" <<endl; } int m_A; }; class Son :public Base{ public : Son (){ m_A=200 ; } void func () cout<<"son的func调用" <<endl; } int m_A; }; void test01 () Son s1; cout<<s1.m_A<<endl; cout<<s1.Base::m_A<<endl; s1.func (); s1.Base::func (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
5.继承中的静态成员处理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Base { public : static int m_A; static void func () cout<<"base func()" <<endl; } static void func (int a) cout<<"base func(int a)" <<endl; } }; int Base::m_A = 10 ;class Son : public Base{ public : static int m_A; static void func () cout<<"son func()" <<endl; } static void func (int a) cout<<"son func(int a)" <<endl; } }; int Son::m_A = 20 ;void test01 () cout << Son::m_A << endl; Son::func (); Son::func (4 ); Son::Base::func (); Son::Base::func (4 ); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
6.多继承的概念以及问题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Base1 { public : Base1 (){ m_A=10 ; } int m_A; }; class Base2 { public : Base2 (){ m_A=20 ; } int m_A; }; class Son :public Base1,public Base2{ public : int m_C; int m_D; }; void test01 () cout<<sizeof (Son)<<endl; Son s1; cout<<s1.Base1::m_A<<endl; cout<<s1.Base2::m_A<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
多继承的语法 :class 派生类:继承方式1 基类1,继承方式2 基类2...{};
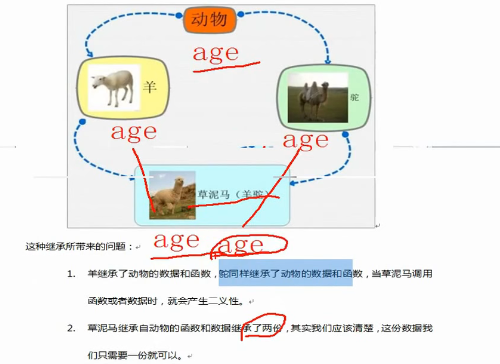
7.菱形继承的问题以及解决方法 两个派生类继承同一个基类而又有某个类同时继承这两个派生类这种继承被称为菱形继承,或者钻石型继承。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Animal { public : int m_Age; }; class Sheep :virtual public Animal{}; class Camel :virtual public Animal{}; class Sheep_Camel :public Sheep,public Camel{}; void test01 () Sheep_Camel sc; sc.Sheep::m_Age=10 ; sc.Camel::m_Age=20 ; cout<<sc.Sheep::m_Age<<endl; cout<<sc.Camel::m_Age<<endl; cout<<sc.m_Age<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
最后全部输出20,因为本质上所有m_Age变成一个了。
8.虚基类的内部工作原理解析(*)
第五章 1.静态联编和动态联编
多态意指相同的消息给予不同的对象会引发不同的动作(一个接口,多种方法)。其实更简单地来说,就是“在用父类指针调用函数时,实际调用的是指针指向的实际类型(子类)的成员函数”。多态性使得程序调用的函数是在运行时动态确定的,而不是在编译时静态确定的。
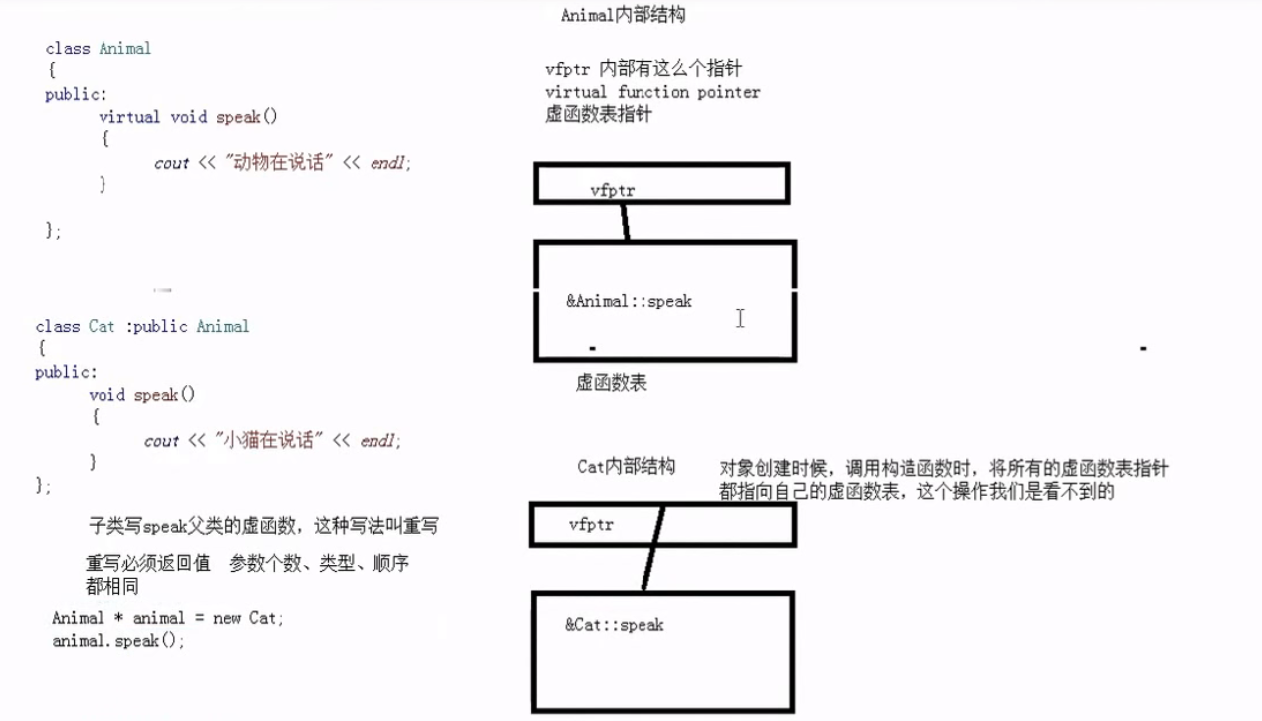
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Animal { public : virtual void speak () cout<<"动物在说话" <<endl; } }; class Cat :public Animal{ public : void speak () cout<<"小猫在说话" <<endl; } }; void dospeak (Animal &animal) animal.speak (); } void test01 () Cat cat1; dospeak (cat1); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.多态原理解析
3.多态深入剖析锻炼
1 2 ((void (*)()) (*(int *)*(int *)animal))(); ((void (*)()) (*((int *)*(int *)animal+1 ))();
4.多态案例—计算器案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Abstract_Calculator { public : int value1; int value2; void setvalue1 (int a) { this ->value1 = a; } void setvalue2 (int b) { this ->value2 = b; } virtual int getResult () { return 0 ; }; }; class Add_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1+value2; }; }; class Cut_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1-value2; }; }; class Cheng_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1*value2; }; }; void test02 () Abstract_Calculator *abc; abc=new Add_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; delete abc; abc=new Cut_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; delete abc; abc=new Cheng_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
5.抽象类和纯虚函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Abstract_Calculator { public : int value1; int value2; void setvalue1 (int a) { this ->value1 = a; } void setvalue2 (int b) { this ->value2 = b; } virtual int getResult () 0 ; }; class Add_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1+value2; }; }; class Cut_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1-value2; }; }; class Cheng_Calculator :public Abstract_Calculator{public : virtual int getResult () return value1*value2; }; }; void test02 () Abstract_Calculator *abc; abc=new Add_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; delete abc; abc=new Cut_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; delete abc; abc=new Cheng_Calculator; abc->setvalue1 (12 ); abc->setvalue2 (10 ); cout<<abc->getResult ()<<endl; } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
6.虚析构和纯虚析构函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <string.h> using namespace std;class Animal { public : virtual ~Animal ()=0 ; virtual void speak () cout<<"动物在说话" <<endl; } }; Animal::~Animal (){ cout<<"Animal纯虚析构函数调用" <<endl; } class Cat :public Animal{ public : char *m_Name; Cat (const char *name){ this ->m_Name=new char [strlen (name)+1 ]; strcpy (this ->m_Name,name); } void speak () cout<<m_Name<<"在讲话" <<endl; } ~Cat (){ cout<<"Cat的析构函数调用" <<endl; if (this ->m_Name!=NULL ){ delete [] this ->m_Name; this ->m_Name=NULL ; } } }; void test01 () Animal *animal=new Cat ("TOM" ); animal->speak (); delete animal; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
7.向上类型转化和向下类型转化 基类转化成派生类(向下类型转化)——>不安全
派生类转化成基类(向上类型转化)——>安全
多态中都是安全的
8.多态案例,PK游戏 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Weapon { public : virtual int getBaseeDamage () 0 ; virtual int geetSuckBlood () 0 ; virtual bool getHold () 0 ; virtual bool getCri () 0 ; string m_WeaponName; int m_BaseDamage; }; class Knife : public Weapon{ Knife () { this ->m_BaseDamage = 10 ; this ->m_WeaponName = "小刀" ; } virtual int getBaseeDamage () { return this ->m_BaseDamage; } virtual int geetSuckBlood () { return 0 ; } virtual bool getHold () { return false ; } virtual bool getCri () { return false ; } }; class DragonSword : public Weapon{ public : DragonSword () { this ->m_BaseDamage = 20 ; this ->m_WeaponName = "屠龙宝刀" ; this ->suckRate = 20 ; this ->holdRate = 30 ; this ->critRate = 35 ; } virtual int getBaseeDamage () { return this ->m_BaseDamage; } virtual int geetSuckBlood () { if (isTrigger (suckRate)) { return m_BaseDamage * 0.5 ; } else { return 0 ; } } virtual bool getHold () { if (isTrigger (holdRate)) { return true ; } else { return false ; } } virtual bool getCri () { if (isTrigger (critRate)) { return true ; } else { return false ; } } int suckRate; int holdRate; int critRate; bool isTrigger (int rate) { int num = rand () % 100 + 1 ; if (num < rate) { return true ; } else { return false ; } } }; class Monster { public : Monster (){ this ->m_Hp=300 ; this ->m_Atk=70 ; this ->m_Def=40 ; this ->m_Hold=false ; this ->m_Name="比克大魔王" ; } string m_Name; int m_Hp; int m_Atk; int m_Def; bool m_Hold; void Attack (Hero *hero) if (this ->m_Hold){ cout<<"怪物" <<this ->m_Name<<"被定身了,本回合无法攻击。" <<endl; return ; } else { int truedamage=(this ->m_Atk-hero->m_Def)>0 ? this ->m_Atk-hero->m_Def:1 ; hero->m_Hp-=truedamage; cout<<"怪物" <<this ->m_Name<<"攻击了英雄" <<hero->m_Name<<"造成了伤害:" <<truedamage<<endl; } } }; class Hero { public : Hero () { this ->m_Hp = 500 ; this ->m_Atk = 50 ; this ->m_Def = 50 ; this ->m_Name = "邪恶小法师" ; this ->weapon = NULL ; } string m_Name; int m_Atk; int m_Def; int m_Hp; Weapon *weapon; void EquipWeapon (Weapon *weapon) { this ->weapon = weapon; cout << "英雄:" << this ->m_Name << "装备" << this ->weapon->m_WeaponName << endl; } void Attack (Monster *monster) { int damage = 0 ; int addHP = 0 ; bool isHold = false ; bool isCrit = false ; if (this ->weapon == NULL ) { damage = this ->m_Atk; } else { damage = this ->weapon->getBaseeDamage () + this ->m_Atk; addHP = this ->weapon->geetSuckBlood (); isHold = this ->weapon->getHold (); isCrit = this ->weapon->getCri (); } if (isCrit) { damage = damage * 2 ; cout << "英雄的武器触发了暴击效果,怪物受到了双倍的伤害,伤害值为:" << damage << endl; } if (isHold) { cout << "英雄的武器触发了定身效果,怪物停止攻击一回合。" << endl; } if (addHP > 0 ) { cout << "英雄的武器触发了吸血效果,英雄增加的血量为:" << addHP << endl; } monster->m_Hold=isHold; int trueDamage=(damage-monster->m_Def)>0 ? damage-monster->m_Def:1 ; monster->m_Hp-=trueDamage; this ->m_Hp+=addHP; cout<<"英雄" <<this ->m_Name<<"攻击了敌人" <<monster->m_Name<<"造成了伤害:" <<trueDamage<<endl; } }; int main () Monster * monster = new Monster; Hero * hero = new Hero; Weapon * kinfe = new Knife; Weapon * dragon = new DragonSword; cout << "请选择武器:" << endl; cout << "1. 赤手空拳" << endl; cout << "2. 小刀" << endl; cout << "3. 屠龙刀" << endl; int oper; cin >> oper; switch (oper) { case 1 : cout << "你真牛X,你还是太年轻了!" << endl; break ; case 2 : hero->EquipWeapon (kinfe); break ; case 3 : hero->EquipWeapon (dragon); break ; } getchar (); int round = 1 ; while (true ) { getchar (); system ("cls" ); cout << "----- 当前第 " << round << " 回合开始 ------" << endl; if (hero->m_Hp <= 0 ) { cout << "英雄 " << hero->m_Name << "已挂 ,游戏结束" << endl; break ; } hero->Attack (monster); if (monster->m_Hp <= 0 ) { cout << "怪物 " << monster->m_Name << "已挂,顺利通关" << endl; break ; } monster->Attack (hero); if (hero->m_Hp <= 0 ) { cout << "英雄 " << hero->m_Name << "已挂 ,游戏结束" << endl; break ; } cout << "英雄 " << hero->m_Name << "剩余血量:" << hero->m_Hp << endl; cout << "怪物 " << monster->m_Name << "剩余血量:" << monster->m_Hp << endl; round++; } delete monster; delete hero; delete kinfe; delete dragon; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
第六章 1.函数模板基本使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T > void Swap (T &a, T &b) T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } void test01 () int a = 10 ; int b = 20 ; Swap (a, b); Swap <int >(a,b); cout << "a:" << a << endl; cout << "b:" << b << endl; double c = 3.14 ; double d = 0.1 ; Swap (c, d); cout << "c:" << c << endl; cout << "d:" << d << endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.实现通用数组排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T >void Swap (T &a, T &b) T temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } template <class T >void MySort (T arry[], int len) for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { int max = i; for (int j = i + 1 ; j < len; j++) { if (arry[max] < arry[j]) { max = j; } } if (max != i) { Swap (arry[max], arry[i]); } } } template <class T >void PrintArray (T arry[], int len) for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { cout << arry[i] << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () char CharArray[] = "helloworld" ; int length = sizeof (CharArray); MySort (CharArray, length); PrintArray (CharArray, length); int IntArray[]={1 ,2 ,3 }; int length1 = sizeof (IntArray)/sizeof (IntArray[1 ]); MySort (IntArray, length1); PrintArray (IntArray, length1); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
3.函数模板与普通函数的区别以及调用规则 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T >T myPuls (T &a,T &b) { return a+b; } int myPUls2 (int a,int b) return a+b; } void test01 () int a=10 ; int b=20 ; char c1='c' ; myPuls (a,b); myPUls2 (a,b); cout<<myPUls2 (a,c1)<<endl; } template <class T >void myprint (T &a,T &b) cout<<"模板函数调用" <<endl; } template <class T >void myprint (T &a,T &b,T &c) cout<<"模板函数调用(a,b,c)" <<endl; } void myprint (int a,int b) cout<<"普通函数调用" <<endl; } void test02 () int a=10 ; int b=20 ; myprint (a,b); myprint<>(a,b); int c=30 ; myprint (a,b,c); char c1='c' ; char d1='d' ; myprint (c1,d1); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
4.模板的机制
5.函数模板的局限性以及解决 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Person { public : int m_Age; string m_Name; Person ( string name,int age) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } }; template <class T >bool Compare_test (T &a, T &b) if (a == b) { return true ; } return false ; } template <>bool Compare_test <Person>(Person &p1, Person &p2){ if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) { return true ; } return false ; } void test01 () int a = 10 ; int b = 20 ; cout<<Compare_test (a,b)<<endl; Person p1 ("Tom" ,10 ) ; Person p2 ("Olivia" ,10 ) ; cout<<Compare_test (p1,p2)<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
6.类模板的基本使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class NameType ,class AgeType >class Person { public : Person (NameType name,AgeType age){ this ->m_Age=age; this ->m_Name=name; } void showPerson () cout<<"姓名:" <<this ->m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<this ->m_Age<<endl; } NameType m_Name; AgeType m_Age; }; void test01 () Person<string,int > p ("孙悟空" ,100 ) ; p.showPerson (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
7.成员函数的创建时机 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Person1 { public : void showPerson1 () { cout << "person1" << endl; } }; class Person2 { public : void showPerson2 () { cout << "person2" << endl; } }; template <class T >class Myclass { public : T object; void func1 () { object.showPerson1 (); } void func2 () { object.showPerson2 (); } }; int main () Myclass<Person1> p1; p1.func1 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
8.类模板做函数参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class NameType ,class AgeType >class Person { public : Person (NameType name,AgeType age){ this ->m_Age=age; this ->m_Name=name; } void showPerson () cout<<"姓名:" <<this ->m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<this ->m_Age<<endl; } NameType m_Name; AgeType m_Age; }; void doWork (Person<string,int > &p) p.showPerson (); } void test01 () Person<string,int > p ("p1" ,10 ) ; doWork (p); } template <class T1 ,class T2 >void doWork2 (Person<T1,T2> &p) p.showPerson (); } void test02 () Person<string,int > p ("p2" ,10 ) ; doWork (p); } template <class T >void doWork3 (T &p) p.showPerson (); } void test03 () Person<string,int > p ("p3" ,10 ) ; doWork3 (p); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
9.类模板碰到继承的问题以及解决 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T >class Base { public : T m_A; }; class Child :public Base<int >{ }; template <class T1 ,class T2 >class Child2 :public Base<T2>{ public : T1 m_B; Child2 () { cout<<typeid (T1).name ()<<endl; cout<<typeid (T2).name ()<<endl; } }; void test01 () Child2<int ,double >child; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
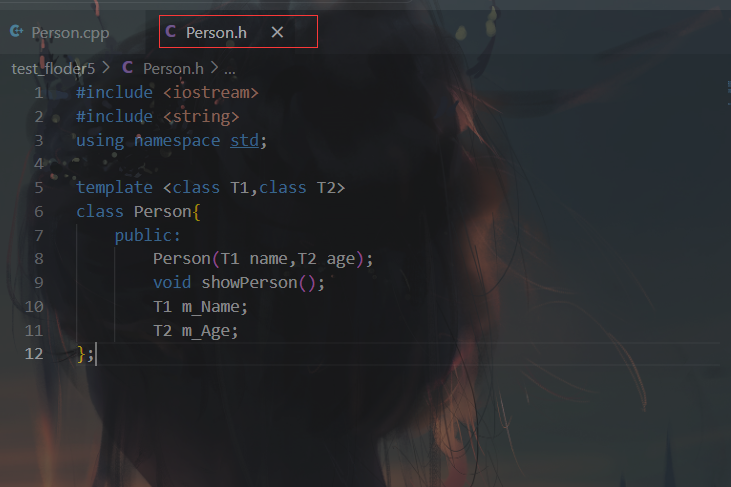
10.类模板的类外实现成员函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T1 ,class T2 >class Person { public : Person (T1 name,T2 age); void showPerson () T1 m_Name; T2 m_Age; }; template <class T1 ,class T2 >Person<T1,T2>::Person (T1 name,T2 age){ this ->m_Name=name; this ->m_Age=age; } template <class T1 ,class T2 >void Person<T1,T2>::showPerson (){ cout<<"姓名:" <<this ->m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<this ->m_Age<<endl; } void test01 () Person<string,int > p1 ("zx" ,18 ) ; p1.showPerson (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
11.类模板的分文件编写问题以及解决
12.友元函数类内实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T1 , class T2 >class Person { public : Person (T1 name, T2 age) { this ->m_Name = name; this ->m_Age = age; }; friend void printPerson (Person<T1,T2> &p) cout<<"姓名:" <<p.m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<p.m_Age<<endl; } private : T1 m_Name; T2 m_Age; }; int main () Person<string,int > p1 ("zx" ,18 ) ; printPerson (p1); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
13.友元函数类外实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T1 , class T2 > class Person ;template <class T1 , class T2 > void printPerson (Person<T1, T2> &p) template <class T1 , class T2 >class Person { public : Person (T1 name, T2 age) { this ->m_Name = name; this ->m_Age = age; }; friend void printPerson<>(Person<T1, T2> &p); private : T1 m_Name; T2 m_Age; }; template <class T1 , class T2 >void printPerson (Person<T1, T2> &p) cout << "姓名:" << p.m_Name << " 年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl; } int main () Person<string, int > p1 ("zx" , 18 ) ; printPerson (p1); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
14.数组类的封装 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;template <class T >class MyArray { public : MyArray (){}; explicit MyArray (int capacity) { this ->m_Capacity = capacity; this ->m_Size = 0 ; this ->pAddress = new T[this ->m_Capacity]; } MyArray (const MyArray &myarray) { this ->m_Capacity = myarray.m_Capacity; this ->m_Size = myarray.m_Size; this ->pAddress = new T[this ->m_Capacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_Size; i++) { this ->pAddress[i] = myarray[i]; } } ~MyArray () { if (this ->pAddress != NULL ) { delete [] this ->pAddress; this ->pAddress = NULL ; } } MyArray& operator =(MyArray &myarray) { if (this ->pAddress != NULL ) { delete [] this ->pAddress; this ->pAddress = NULL ; } this ->m_Capacity = myarray.m_Capacity; this ->m_Size = myarray.m_Size; this ->pAddress = new T[this ->m_Capacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < this ->m_Size; i++) { this ->pAddress[i] = myarray[i]; } } T& operator [](int index){ return this ->pAddress[index]; } void Push_Back (T val) this ->pAddress[this ->m_Size]=val; this ->m_Size++; } int getSize () return this ->m_Size; } int getCapacity () return this ->m_Capacity; } private : T *pAddress; int m_Capacity; int m_Size; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include "MyArray.hpp" void printIntArray (MyArray<int > &arr) for (int i=0 ;i<arr.getSize ();i++){ cout<<arr[i]<<endl; } } class Person { public : Person (){}; Person (string name,int age){ this ->m_Name=name; this ->m_Age=age; } string m_Name; int m_Age; }; void printPersonArray (MyArray<Person> &array) for (int i=0 ;i<array.getSize ();i++){ cout<<"姓名: " <<array[i].m_Name<<" 年龄: " <<array[i].m_Age<<endl; } } int main () MyArray<int > arr (10 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ arr.Push_Back (i+10 ); } printIntArray (arr); Person p1 ("zx" ,18 ) ; Person p2 ("zwh" ,18 ) ; MyArray<Person> arr2 (10 ) ; arr2.Push_Back (p1); arr2.Push_Back (p2); printPersonArray (arr2); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
第七章 1.静态类型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () char a='a' ; double d=static_cast <double >(a); cout<<"d: " <<d<<endl; } class Base {};class Child :public Base{};class Other {};void test02 () Base* base=NULL ; Child* child=NULL ; Child* child2=static_cast <Child*>(base); Base* base2=static_cast <Base*>(child); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.动态类型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () char a = 'a' ; double d = static_cast <double >(a); cout << "d: " << d << endl; } class Base { }; class Child : public Base{ }; class Other { }; void test02 () Base *base = NULL ; Child *child = NULL ; Child *child2 = static_cast <Child *>(base); Base *base2 = static_cast <Base *>(child); } void test03 () char c = 'a' ; } class Base2 { public : virtual void func () }; class Child2 : public Base2{ public : virtual void func () }; class Other2 { }; void test02 () Base2 *base = NULL ; Child2 *child = NULL ; Base2* base3=new Child2; Child2* child3 = dynamic_cast <Child2*>(base3); Base2 *base2 =dynamic_cast <Base2 *>(child); } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
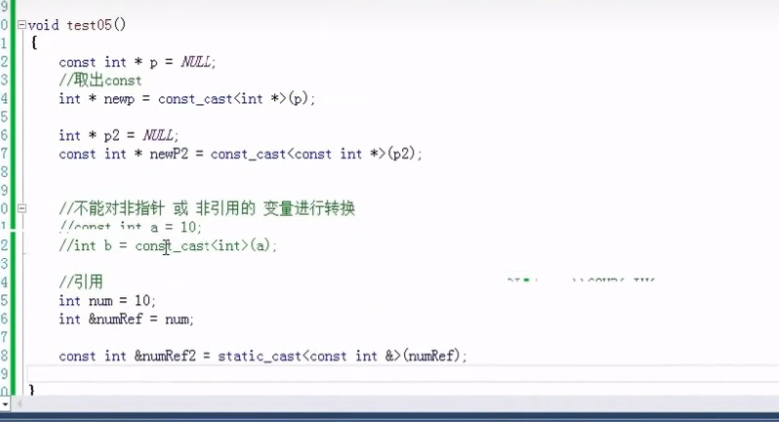
3.常量转化和重新解释转化 注意:不能直接对非指针和非引用的变量使用const cast操作符去直接移除它的const
4.异常的基本使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;int myDevide (int a,int b) if (b==0 ){ throw 3.14 ; } return a/b; } void test01 () int a=10 ; int b=0 ; try { myDevide (a,b); } catch (int ){ cout<<"int类型异常捕获" <<endl; } catch (double ){ cout<<"double类型异常捕获" <<endl; } catch (...){ cout<<"其他类型异常捕获" <<endl; } } int main () try { test01 (); } catch (double ){ cout<<"main double类型异常捕获" <<endl; } system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
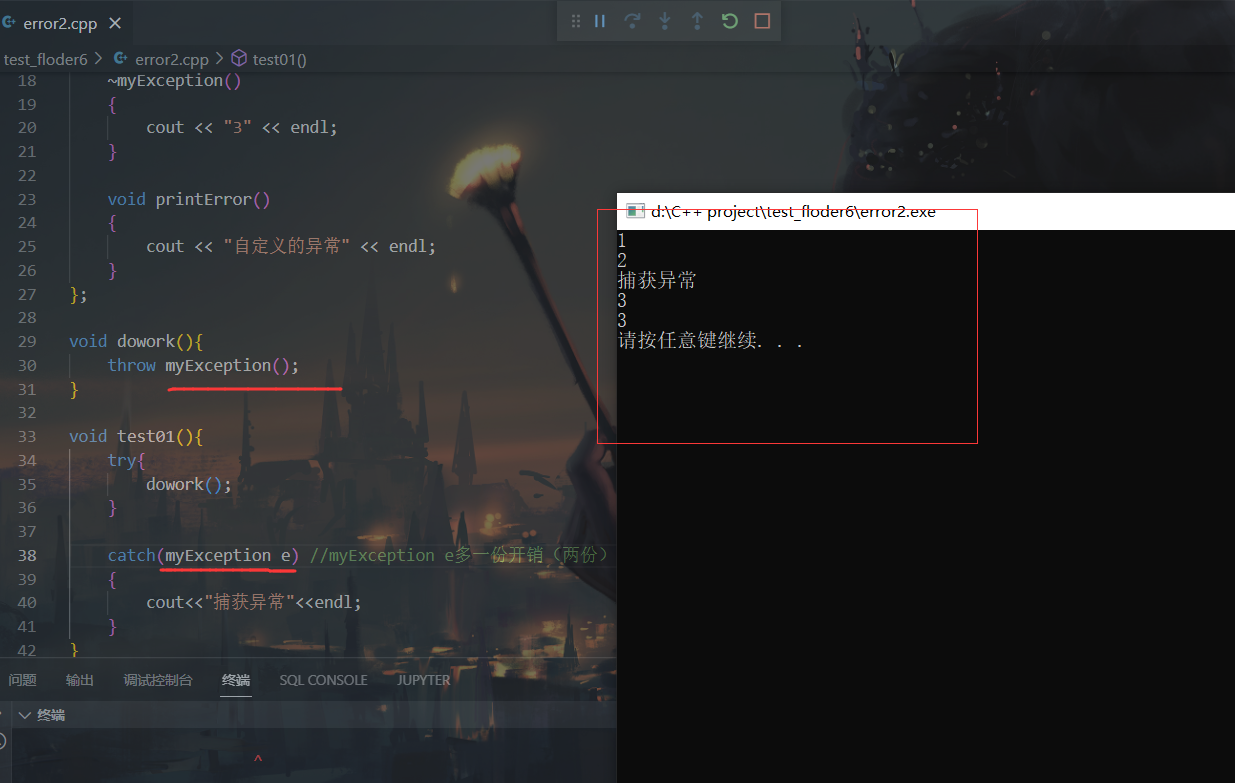
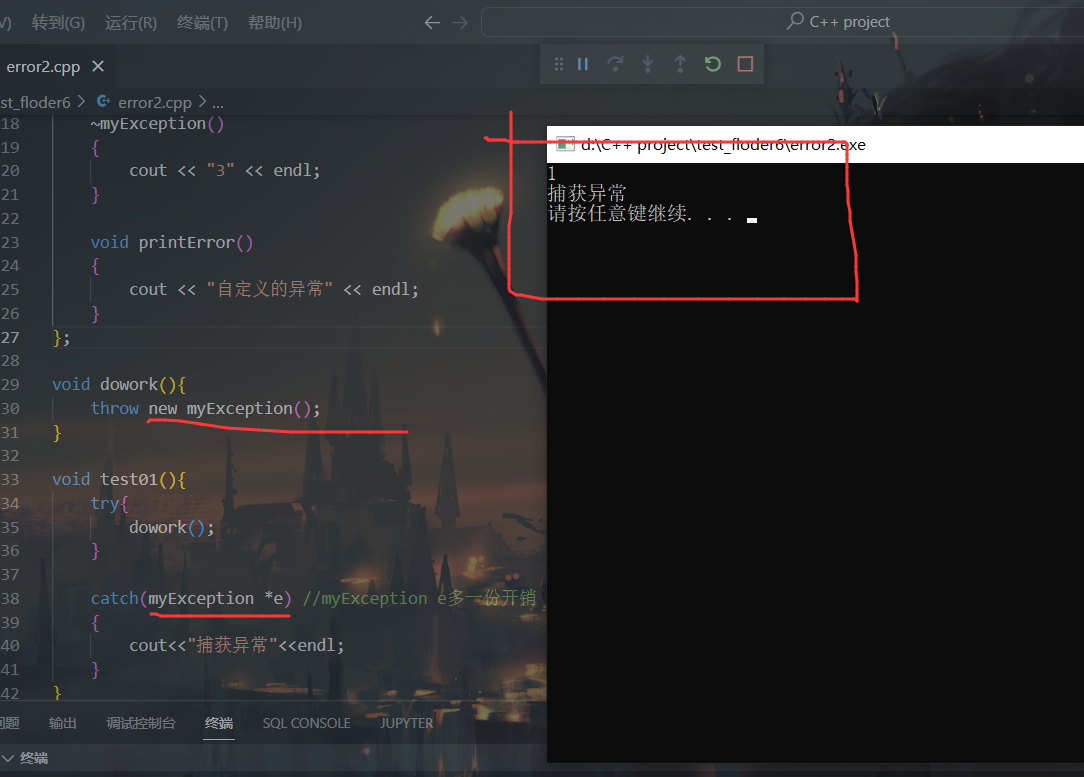
5.自定义异常类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class myException { public : void printError () { cout << "自定义的异常" << endl; } }; int myDevide (int a, int b) if (b == 0 ) { myException e; throw e; } return a / b; } void test01 () int a = 10 ; int b = 0 ; try { myDevide (a, b); } catch (int ) { cout << "int类型异常捕获" << endl; } catch (double ) { cout << "double类型异常捕获" << endl; } catch (myException e) { e.printError (); } catch (...) { cout << "其他类型异常捕获" << endl; } } int main () try { test01 (); } catch (double ) { cout << "main double类型异常捕获" << endl; } system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
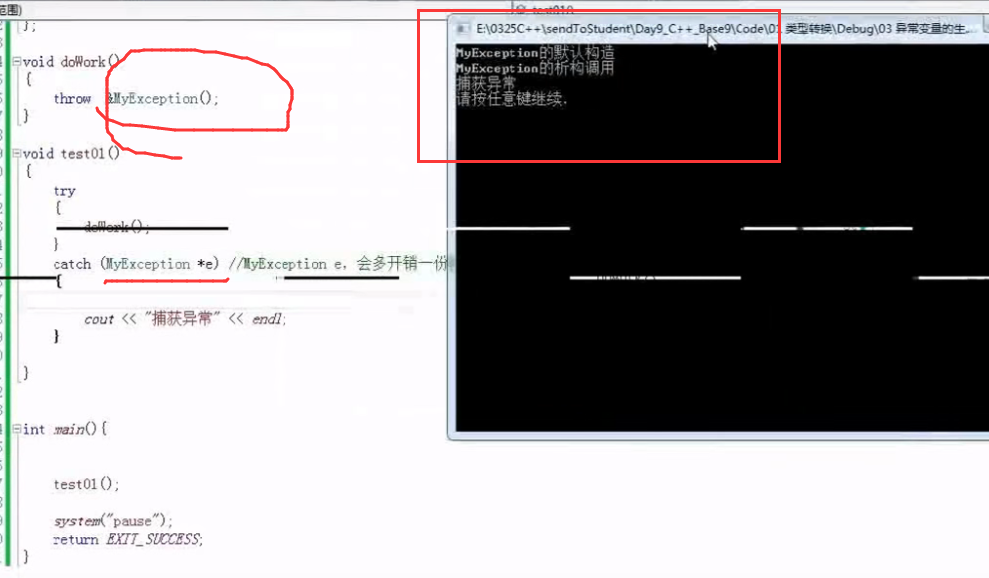
6.栈解旋 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class myException { public : void printError () { cout << "自定义的异常" << endl; } }; class Person { public : Person (){ cout<<"1" <<endl; } ~Person (){ cout<<"2" <<endl; } }; int myDevide (int a, int b) if (b == 0 ) { Person p1; Person p2; myException e; throw e; } return a / b; } void test01 () int a = 10 ; int b = 0 ; try { myDevide (a, b); } catch (int ) { cout << "int类型异常捕获" << endl; } catch (double ) { cout << "double类型异常捕获" << endl; } catch (myException e) { e.printError (); } catch (...) { cout << "其他类型异常捕获" << endl; } } int main () try { test01 (); } catch (double ) { cout << "main double类型异常捕获" << endl; } system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
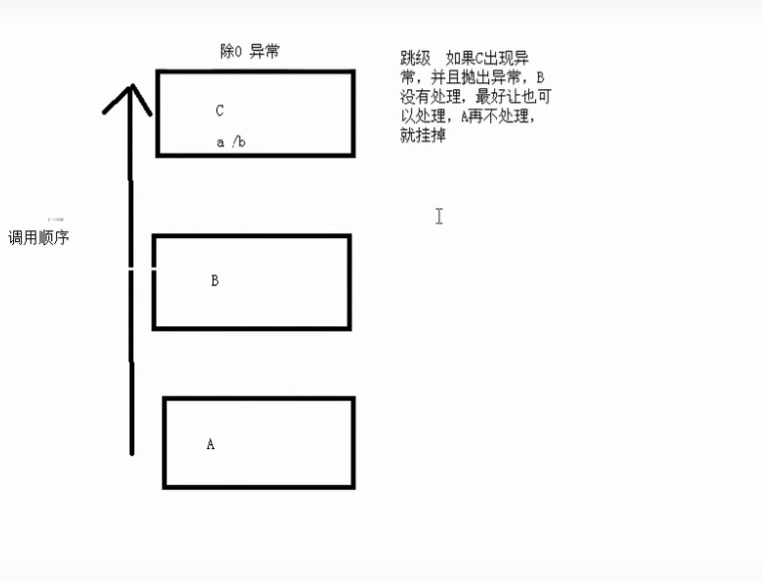
7.异常的接口声明 如果想抛出特定的类型异常,可以利用异常的接口声明void func() throw ( int)只能抛出int类型,throw()不抛出异常。
8.异常的生命周期
推荐使用引用的方式
9.异常的多态使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class BaseException { public : virtual void printError () }; class NULLException :public BaseException{ public : virtual void printError () cout<<"空指针异常" <<endl; }; }; class IndexException :public BaseException{ public : virtual void printError () cout<<"越界异常" <<endl; }; }; void dowork () throw IndexException (); } void test01 () try { dowork (); } catch (BaseException &e){ e.printError (); } } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
10.使用系统标准异常 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <stdexcept> class Person { public : int m_Age; string m_Name; Person (string name,int age){ if (age<=0 || age>=120 ){ throw length_error ("长度越界。" ); } else { this ->m_Age=age; this ->m_Name=name; } } }; void test01 () try { Person p1 ("zx" ,150 ) ; } catch (out_of_range &e){ cout<<e.what ()<<endl; } catch (length_error &e){ cout<<e.what ()<<endl; } } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
11.编写自己的异常类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class MyErrorException : public exception{ public : string errorInfo; MyErrorException (string error) { this ->errorInfo = error; } ~MyErrorException () { cout << "析构函数" << endl; } virtual const char * what () const _GLIBCXX_TXN_SAFE_DYN _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT { return this ->errorInfo.c_str (); } }; class Person { public : int m_Age; string m_Name; Person (string name, int age) { if (age <= 0 || age >= 120 ) { throw MyErrorException (string ("长度越界。" )); } else { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } } }; void test01 () try { Person p1 ("zx" ,150 ) ; } catch (MyErrorException &e){ cout<<e.what ()<<endl; } } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
12.标准输入流 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () char c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; } void test02 () char buf[1024 ]; cin.get (buf, 1024 ); char c = cin.get (); if (c == '\n' ) { cout << "换行还在缓冲区域" << endl; } else { cout << "换行不在缓冲区域" << endl; } cout << buf << endl; } void test03 () char buf[1024 ]; cin.getline (buf, 1024 ); char c = cin.get (); if (c == '\n' ) { cout << "换行还在缓冲区域" << endl; } else { cout << "换行不在缓冲区域" << endl; } cout << buf << endl; } void test04 () cin.ignore (); char c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; } void test05 () char c = cin.peek (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout<< "c=" << c << endl; } void test06 () char c=cin.get (); cin.putback (c); char buf[1024 ]; cin.getline (buf,1024 ); cout<<buf<<endl; } int main () test06 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
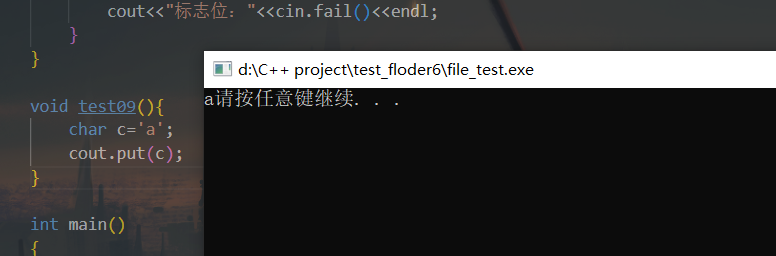
13.案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () char c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; } void test02 () char buf[1024 ]; cin.get (buf, 1024 ); char c = cin.get (); if (c == '\n' ) { cout << "换行还在缓冲区域" << endl; } else { cout << "换行不在缓冲区域" << endl; } cout << buf << endl; } void test03 () char buf[1024 ]; cin.getline (buf, 1024 ); char c = cin.get (); if (c == '\n' ) { cout << "换行还在缓冲区域" << endl; } else { cout << "换行不在缓冲区域" << endl; } cout << buf << endl; } void test04 () cin.ignore (); char c = cin.get (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; } void test05 () char c = cin.peek (); cout << "c=" << c << endl; c = cin.get (); cout<< "c=" << c << endl; } void test06 () char c=cin.get (); cin.putback (c); char buf[1024 ]; cin.getline (buf,1024 ); cout<<buf<<endl; } void test07 () cout<<"请输入一串数字或者字符串" <<endl; char c=cin.peek (); if (c>='0' && c<='9' ){ int num; cin>>num; cout<<"你输入是数字:" <<num<<endl; } else { char buf[1024 ]; cin>>buf; cout<<"你输入是字符串:" <<buf<<endl; } } void test08 () cout<<"请输入一个1-10的数字:" <<endl; int num; while (true ){ cin>>num; if (num>0 && num<=10 ){ cout<<"你输入是数字:" <<num<<endl; break ; } cin.clear (); cin.sync (); cout<<"标志位:" <<cin.fail ()<<endl; } } int main () test08 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
14.标准输出流
15 文件操作 程序运行时产生的数据都属于临时数据,程序一旦运行结束都会被释放
通过文件可以将数据持久化
C++中对文件操作需要包含头文件 < fstream >
文件类型分为两种:
文本文件 - 文件以文本的ASCII码 形式存储在计算机中二进制文件 - 文件以文本的二进制 形式存储在计算机中,用户一般不能直接读懂它们
操作文件的三大类:
ofstream:写操作
ifstream: 读操作
fstream : 读写操作
15.1文本文件 15.1.1写文件 写文件步骤如下:
包含头文件
#include
创建流对象
ofstream ofs;
打开文件
ofs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
写数据
ofs << “写入的数据”;
关闭文件
ofs.close();
文件打开方式:
打开方式
解释
ios::in
为读文件而打开文件
ios::out
为写文件而打开文件
ios::ate
初始位置:文件尾
ios::app
追加方式写文件
ios::trunc
如果文件存在先删除,再创建
ios::binary
二进制方式
注意: 文件打开方式可以配合使用,利用|操作符
例如: 用二进制方式写文件 ios::binary | ios:: out
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> #include <fstream> int main () std::ofstream outfile; outfile.open ("test_text.txt" , std::ios::out); outfile << "姓名:张三" << std::endl; outfile << "年龄:18岁" << std::endl; outfile << "性别:男" << std::endl; outfile.close (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
总结:
文件操作必须包含头文件 fstream
读文件可以利用 ofstream ,或者fstream类
打开文件时候需要指定操作文件的路径,以及打开方式
利用<<可以向文件中写数据
操作完毕,要关闭文件
15.1.2读文件 读文件与写文件步骤相似,但是读取方式相对于比较多
读文件步骤如下:
包含头文件
#include
创建流对象
ifstream ifs;
打开文件并判断文件是否打开成功
ifs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
读数据
四种方式读取
关闭文件
ifs.close();
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <string> void test01 () std::ifstream ifs; ifs.open ("test_text.txt" , std::ios::in); if (!ifs.is_open ()) { std::cout << "文件打开失败" << std::endl; } char c; while ((c = ifs.get ()) != EOF) { std::cout << c; } ifs.close (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
总结:
读文件可以利用 ifstream ,或者fstream类
利用is_open函数可以判断文件是否打开成功
close 关闭文件
15.2 二进制文件 以二进制的方式对文件进行读写操作
打开方式要指定为 ios::binary
15.2.1 写文件 二进制方式写文件主要利用流对象调用成员函数write
函数原型 :ostream& write(const char * buffer,int len);
参数解释:字符指针buffer指向内存中一段存储空间。len是读写的字节数
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <iostream> class Person { public : char m_Name[64 ]; int m_Age; }; void test01 () std::ofstream ofs ("person.txt" , std::ios::out | std::ios::binary) ; Person p = {"张三" , 18 }; ofs.write ((const char *)&p, sizeof (p)); ofs.close (); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
总结:
文件输出流对象 可以通过write函数,以二进制方式写数据
15.2.2 读文件 二进制方式读文件主要利用流对象调用成员函数read
函数原型:istream& read(char *buffer,int len);
参数解释:字符指针buffer指向内存中一段存储空间。len是读写的字节数
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <iostream> class Person { public : char m_Name[64 ]; int m_Age; }; void test01 () std::ifstream ifs ("person.txt" , std::ios::in | std::ios::binary) ; if (!ifs.is_open ()) { std::cout << "文件打开失败" << std::endl; } Person p; ifs.read ((char *)&p, sizeof (p)); std::cout << "姓名: " << p.m_Name << " 年龄: " << p.m_Age << std::endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
文件输入流对象 可以通过read函数,以二进制方式读数据
第八章 前面几节视频都是概念,这后面开始才是实践。
1.三大组件初识 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () int array[5 ] = {1 , 3 , 5 , 3 , 6 }; int *p = array; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { cout << *(p++) << endl; cout << array[i] << endl; } } #include <vector> void test02 () vector<int > a; a.push_back (12 ); a.push_back (42 ); a.push_back (52 ); a.push_back (15 ); vector<int >::iterator it_begin=a.begin (); vector<int >::iterator it_end=a.end (); while (it_begin!=it_end) { cout<<*it_begin<<endl; it_begin++; } } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.三大组件的基本使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <algorithm> void test01 () int array[5 ] = {1 , 3 , 5 , 3 , 6 }; int *p = array; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { cout << *(p++) << endl; cout << array[i] << endl; } } #include <vector> void myprint (int v) cout << v << endl; } class Person { public : Person (string name, int age) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } string m_Name; int m_Age; }; void test02 () vector<int > a; a.push_back (12 ); a.push_back (42 ); a.push_back (52 ); a.push_back (15 ); vector<int >::iterator it_begin = a.begin (); vector<int >::iterator it_end = a.end (); for (vector<int >::iterator it = a.begin (); it != a.end (); it++) { cout << *it << endl; } for_each(it_begin, it_end, myprint); } void test03 () vector<Person *> v2; Person p1 ("zx" , 18 ) ; Person p2 ("zwh" , 20 ) ; v2.push_back (&p1); v2.push_back (&p2); for (vector<Person *>::iterator it = v2.begin (); it != v2.end (); it++) { cout << "姓名:" << (*it)->m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it)->m_Age << endl; } } void test05 () vector<vector<int >> v; vector<int > v1; vector<int > v2; vector<int > v3; vector<int > v4; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { v1.push_back (i); v2.push_back (i); v3.push_back (i); v4.push_back (i); } v.push_back (v1); v.push_back (v2); v.push_back (v3); v.push_back (v4); for ( vector<vector<int >>::iterator it=v.begin (); it != v.end (); it++){ for (vector<int >::iterator it_i=(*it).begin (); it_i!= (*it).end (); it_i++){ cout<<*it_i<<endl; } } } int main () test05 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
3.string 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test01 () string str; string str2 (str) ; string str3=str; string str4="abcd" ; string str5 (10 ,'a' ) ; cout<<str4<<" " <<str5<<endl; str="hello" ; str2=str4; str3.assign ("abcdef" ,4 ); string str6; str6.assign (str,1 ,3 ); cout<<str3<<" " <<str6<<endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
4.string容器API 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <stdexcept> void test01 () string s1 = "我" ; string s2 = "爱北京" ; s1 += s2; cout << s1 << endl; s1.append ("天安门" ); cout << s1 << endl; string s = "abcdefg" ; int pos = s.find ("bc" ); cout << "pos:" << pos << endl; string s3 = "hello" ; s3.replace (1 , 3 , "1111" ); cout << s3 << endl; } void test02 () string s3 = "hello" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s3.size (); i++) { cout << s3.at (i) << endl; } try { cout << s3[10 ] << endl; } catch (out_of_range &e) { cout << e.what () << endl; } catch (...) { cout << "index error!" << endl; } } void test03 () string s1 = "bbc" ; string s2 = "abc" ; if (s1.compare (s2) == 0 ) { cout << "s1=s2" << endl; } else if (s1.compare (s2) >= 0 ) { cout << "s1>=s2" << endl; } else { cout << "s1<=s2" << endl; } } void test04 () string s1 = "abcde" ; string s2 = s1.substr (1 , 3 ); cout << "s2= " << s2 << endl; string email = "zhouxing945@gmail.com" ; int pos = email.find ("@" ); string username = email.substr (0 , pos); cout << "username=" << username << endl; } void test05 () string s1 = "hello" ; s1.insert (1 , "111" ); cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl; s1.erase (1 , 3 ); cout << "s1=" << s1 << endl; } void test06 () } int main () test05 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
5.vector容器 上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std;void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ v.push_back (i); cout<<"campacity=" <<v.capacity ()<<endl; } } void PrintVector (vector<int > v) for (vector<int >::iterator it=v.begin ();it!=v.end ();it++){ cout<<*it<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } void test02 () vector<int > v; int arr[]={2 ,3 ,4 ,1 ,9 }; vector<int > v1 (arr,arr+sizeof (arr)/sizeof (int )) ; vector<int > v2 (v1.begin(),v1.end()) ; PrintVector (v2); vector<int > v3 (10 ,100 ) ; PrintVector (v3); vector<int > v4; v4.assign (v3.begin (),v3.end ()); PrintVector (v4); v4.swap (v2); cout<<"交换V4" <<endl; PrintVector (v4); cout<<"v4.size=" <<v4.size ()<<endl; if (v4.empty ()){ cout<<"empty!" <<endl; } else { cout<<"No empty!" <<endl; } v4.resize (10 ,-1 ); PrintVector (v4); v4.resize (3 ); PrintVector (v4); } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
6.swap收缩空间 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std;void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; v.resize (3 ); cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; vector <int > (v).swap (v); cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
swap收缩空间,先声明了一个匿名对象vector (v)———>你可以理解成有一个对象x,x和v交换指针,x原先指向的地址capacity和size都为3。
7.vector容器 下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std;void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; v.resize (3 ); cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; vector <int >(v).swap (v); cout << "v容量=" << v.capacity () << endl; cout << "v大小=" << v.size () << endl; } void PrintVector (vector<int > v) for (vector<int >::iterator it = v.begin (); it != v.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test02 () vector<int > v; v.push_back (10 ); v.push_back (20 ); v.push_back (30 ); v.push_back (40 ); cout << "v的front" << v.front () << endl; cout << "v的back" << v.back () << endl; v.insert (v.begin (), 100 ); PrintVector (v); v.pop_back (); PrintVector (v); v.erase (v.begin ()); PrintVector (v); for (vector<int >::reverse_iterator it = v.rbegin (); it != v.rend (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; v.erase (v.begin (), v.end ()); PrintVector (v); } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
8.deque容器 要包含头文件
9.sort使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;int main () int num[10 ] = {6 ,5 ,9 ,1 ,2 ,8 ,7 ,3 ,4 ,0 }; sort (num,num+10 ,greater<>()); for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ cout<<num[i]<<" " ; } system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;bool cmp (int a, int b) return a > b; } int main () int a[]={33 ,12 ,20 ,66 ,90 ,11 ,20 ,4 ,5 ,50 }; sort (a, a+10 , cmp); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) printf ("%d " ,a[i]); return 0 ; }
10.stack栈容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <stack> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test () stack<int > s; s.push (10 ); s.push (20 ); s.push (30 ); while (s.size () != 0 ) { cout << "栈顶:" << s.top () << endl; s.pop (); } cout << "size=" << s.size () << endl; } int main () test (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
11.queue队容器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test () queue<int > q; q.push (10 ); q.push (20 ); q.push (30 ); while (!q.empty ()){ cout<<"队头:" <<q.front ()<<endl; cout<<"队尾:" <<q.back ()<<endl; q.pop (); } cout << "size=" << q.size () << endl; } int main () test (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
12.List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <list> using namespace std;void printList (list<int > L) for (list<int >::iterator it = L.begin (); it != L.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () list<int > L (10 , 15 ) ; list<int > L2 (L.begin(), L.end()) ; printList (L); printList (L2); L2.push_back (115 ); for (list<int >::reverse_iterator it = L2.rbegin (); it != L2.rend (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test02 () list<int > L3; L3.push_back (10 ); L3.push_back (20 ); L3.push_back (30 ); L3.push_front (300 ); L3.push_front (400 ); L3.push_front (200 ); printList (L3); cout << "L3.size=" << L3.size () << endl; if (L3.empty ()) { cout << "empty l3" << endl; } else { cout << "l3 no empty" << endl; } L3.resize (10 ); printList (L3); L3.resize (3 ); printList (L3); L3.pop_front (); L3.pop_back (); printList (L3); L3.remove (15 ); } void test03 () list<int > L3; L3.push_back (10 ); L3.push_back (20 ); L3.push_back (30 ); L3.push_front (300 ); L3.reverse (); printList (L3); L3.sort (); printList (L3); } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <list> class Person { public : string m_Name; int m_Age; int m_Height; Person (string name, int age, int height) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Height = height; this ->m_Name = name; } }; void printPersonlist (list<Person> L) for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin (); it != L.end (); it++) { cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << " 身高:" << (*it).m_Height << endl; } } bool compare (Person &p1, Person &p2) if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) { return p1.m_Height < p2.m_Height; } else { return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age; } } void test01 () list<Person> L; Person p1 ("zx" , 18 , 168 ) ; Person p2 ("cbl" , 18 , 172 ) ; Person p3 ("cjl" , 19 , 165 ) ; Person p4 ("hjj" , 20 , 172 ) ; Person p5 ("cwq" , 20 , 177 ) ; L.push_back (p1); L.push_back (p2); L.push_back (p3); L.push_back (p4); L.push_back (p5); L.sort (compare); printPersonlist (L); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
13.list容器remove自定义数据类型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <list> class Person { public : string m_Name; int m_Age; int m_Height; Person (string name, int age, int height) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Height = height; this ->m_Name = name; } bool operator ==(const Person &p){ if (this ->m_Name==p.m_Name && this ->m_Age==p.m_Age && this ->m_Height==p.m_Height){ return true ; } else { return false ; } } }; void printPersonlist (list<Person> L) for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin (); it != L.end (); it++) { cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << " 身高:" << (*it).m_Height << endl; } } bool compare (Person &p1, Person &p2) if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) { return p1.m_Height < p2.m_Height; } else { return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age; } } void test01 () list<Person> L; Person p1 ("zx" , 18 , 168 ) ; Person p2 ("cbl" , 18 , 172 ) ; Person p3 ("cjl" , 19 , 165 ) ; Person p4 ("hjj" , 20 , 172 ) ; Person p5 ("cwq" , 20 , 177 ) ; L.push_back (p1); L.push_back (p2); L.push_back (p3); L.push_back (p4); L.push_back (p5); L.sort (compare); printPersonlist (L); cout<<"--------------------" <<endl; L.remove (p1); printPersonlist (L); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
14.set容器上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <set> void printSet (set<int > &s) for (set<int >::iterator it=s.begin ();it!=s.end ();it++){ cout<<*it<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } void test01 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (4 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); printSet (s1); if (s1.empty ()){ cout<<"empty" <<endl; } else { cout<<"no empty" <<endl; cout<<"size=" <<s1.size ()<<endl; } s1.erase (s1.begin ()); s1.erase (4 ); printSet (s1); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
15.set容器中 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <set> void printSet (set<int > &s) for (set<int >::iterator it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (4 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); printSet (s1); if (s1.empty ()) { cout << "empty" << endl; } else { cout << "no empty" << endl; cout << "size=" << s1.size () << endl; } s1.erase (s1.begin ()); s1.erase (4 ); printSet (s1); } void test02 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); printSet (s1); set<int >::iterator it = s1.find (9 ); if (it != s1.end ()) { cout << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到" << endl; } int count_result = s1.count (10 ); cout << "count_result=" << count_result << endl; set<int >::iterator it_result = s1.lower_bound (3 ); if (it_result != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } set<int >::iterator it_result1 = s1.lower_bound (10 ); if (it_result1 != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result1 << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator,set<int >::iterator> ret=s1.equal_range (3 ); cout<<*(ret.first)<<endl; cout<<*(ret.second)<<endl; } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
16.pair队组的创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <set> void printSet (set<int > &s) for (set<int >::iterator it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (4 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); printSet (s1); if (s1.empty ()) { cout << "empty" << endl; } else { cout << "no empty" << endl; cout << "size=" << s1.size () << endl; } s1.erase (s1.begin ()); s1.erase (4 ); printSet (s1); } void test02 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); printSet (s1); set<int >::iterator it = s1.find (9 ); if (it != s1.end ()) { cout << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到" << endl; } int count_result = s1.count (10 ); cout << "count_result=" << count_result << endl; set<int >::iterator it_result = s1.lower_bound (3 ); if (it_result != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } set<int >::iterator it_result1 = s1.lower_bound (10 ); if (it_result1 != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result1 << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator,set<int >::iterator> ret=s1.equal_range (3 ); cout<<*(ret.first)<<endl; cout<<*(ret.second)<<endl; } void test03 () pair<string,int > p (string("zx" ),18 ) ; cout<<"姓名:" <<p.first<<" 年龄:" <<p.second<<endl; pair<string,int > p1=make_pair ("zwh" ,18 ); cout<<"姓名:" <<p1.first<<" 年龄:" <<p1.second<<endl; } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
17.set容器下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <set> void printSet (set<int > &s) for (set<int >::iterator it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (4 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); printSet (s1); if (s1.empty ()) { cout << "empty" << endl; } else { cout << "no empty" << endl; cout << "size=" << s1.size () << endl; } s1.erase (s1.begin ()); s1.erase (4 ); printSet (s1); } void test02 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); printSet (s1); set<int >::iterator it = s1.find (9 ); if (it != s1.end ()) { cout << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到" << endl; } int count_result = s1.count (10 ); cout << "count_result=" << count_result << endl; set<int >::iterator it_result = s1.lower_bound (3 ); if (it_result != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } set<int >::iterator it_result1 = s1.lower_bound (10 ); if (it_result1 != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result1 << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator, set<int >::iterator> ret = s1.equal_range (3 ); cout << *(ret.first) << endl; cout << *(ret.second) << endl; } void test03 () pair<string, int > p (string("zx" ), 18 ) ; cout << "姓名:" << p.first << " 年龄:" << p.second << endl; pair<string, int > p1 = make_pair ("zwh" , 18 ); cout << "姓名:" << p1.first << " 年龄:" << p1.second << endl; } void test04 () set<int > s2; pair<set<int >::iterator, bool > ret = s2.insert (10 ); if (ret.second != false ) { cout << "success" << endl; } else { cout << "failed" << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator, bool > ret2 = s2.insert (10 ); if (ret2.second != false ) { cout << "success" << endl; } else { cout << "failed" << endl; } } class myCompare { public : bool operator () (int v1,int v2) const { return v1>v2; } }; void test05 () set<int ,myCompare> s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); for (set<int ,myCompare>::iterator it = s1.begin (); it != s1.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } int main () test05 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
18.set容器自定义数据类型插入 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <set> void printSet (set<int > &s) for (set<int >::iterator it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (4 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); printSet (s1); if (s1.empty ()) { cout << "empty" << endl; } else { cout << "no empty" << endl; cout << "size=" << s1.size () << endl; } s1.erase (s1.begin ()); s1.erase (4 ); printSet (s1); } void test02 () set<int > s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); printSet (s1); set<int >::iterator it = s1.find (9 ); if (it != s1.end ()) { cout << *it << endl; } else { cout << "未找到" << endl; } int count_result = s1.count (10 ); cout << "count_result=" << count_result << endl; set<int >::iterator it_result = s1.lower_bound (3 ); if (it_result != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } set<int >::iterator it_result1 = s1.lower_bound (10 ); if (it_result1 != s1.end ()) { cout << *it_result1 << endl; } else { cout << "..." << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator, set<int >::iterator> ret = s1.equal_range (3 ); cout << *(ret.first) << endl; cout << *(ret.second) << endl; } void test03 () pair<string, int > p (string("zx" ), 18 ) ; cout << "姓名:" << p.first << " 年龄:" << p.second << endl; pair<string, int > p1 = make_pair ("zwh" , 18 ); cout << "姓名:" << p1.first << " 年龄:" << p1.second << endl; } void test04 () set<int > s2; pair<set<int >::iterator, bool > ret = s2.insert (10 ); if (ret.second != false ) { cout << "success" << endl; } else { cout << "failed" << endl; } pair<set<int >::iterator, bool > ret2 = s2.insert (10 ); if (ret2.second != false ) { cout << "success" << endl; } else { cout << "failed" << endl; } } class myCompare { public : bool operator () (const int v1,const int v2) const { return v1 > v2; } }; void test05 () set<int , myCompare> s1; s1.insert (5 ); s1.insert (3 ); s1.insert (1 ); s1.insert (9 ); s1.insert (7 ); for (set<int , myCompare>::iterator it = s1.begin (); it != s1.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } class Person { public : string m_Name; int m_Age; Person (string name, int age) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } }; class mycomparePerson {public : bool operator () (const Person &p1,const Person &p2) const { if (p1.m_Age>p2.m_Age){ return true ; } else { return false ; } } }; void test06 () set<Person,mycomparePerson> s1; Person p1 ("zx" , 18 ) ; Person p3 ("cjl" , 19 ) ; Person p5 ("cwq" , 20 ) ; s1.insert (p1); s1.insert (p3); s1.insert (p5); for (set<Person,mycomparePerson>::iterator it = s1.begin (); it != s1.end (); it++) { cout<<"姓名:" <<(*it).m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<(*it).m_Age <<endl; } } int main () test06 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
multiset容器允许插入多个相同的值
set容器不行
19.map容器
20.stl使用时机
、
21.员工分组案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <vector> #include <map> #include <ctime> #define CEHUA 0 #define MEISHU 1 #define YANFA 2 class Worker { public : string m_Name; int m_Salary; }; void createWorker (vector<Worker> &v) string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { Worker worker; worker.m_Name = "员工" ; worker.m_Name = worker.m_Name + nameSeed[i]; worker.m_Salary = rand () % 10000 + 10000 ; v.push_back (worker); } } void setGroup (vector<Worker> &v, multimap<int , Worker> &m) for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = v.begin (); it != v.end (); it++) { int depId = rand () % 3 ; m.insert (make_pair (depId, *it)); } } void showWorkerByGroup (multimap<int , Worker> &m) for (auto it=m.begin ();it!=m.end ();it++){ cout <<"部门标号" <<it->first<<" 姓名:" << it->second.m_Name << " 工资:" << it->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout<<endl; multimap<int , Worker>::iterator pos = m.find (CEHUA); int count = m.count (CEHUA); int index = 0 ; cout << "策划部门" << endl; for (; pos != m.end () && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout<<endl; cout << "美术部门" << endl; pos = m.find (MEISHU); count = m.count (MEISHU); index = 0 ; for (; pos != m.end () && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } cout<<endl; cout << "研发部门" << endl; pos = m.find (YANFA); count = m.count (YANFA); index = 0 ; for (; pos != m.end () && index < count; pos++, index++) { cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl; } } int main () vector<Worker> vWorker; createWorker (vWorker); multimap<int , Worker> mWorker; setGroup (vWorker, mWorker); showWorkerByGroup (mWorker); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
第九章 1.函数对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Myprint { public : int count = 0 ; void operator () (int num) { cout << "num=" << num << endl; count++; } }; void Myprint2 (int num) cout << "num=" << num << endl; } void test01 () Myprint myprint; myprint (10 ); Myprint ()(100 ); Myprint2 (111 ); } void test02 () Myprint myprint; myprint (10 ); myprint (10 ); myprint (10 ); myprint (10 ); myprint (10 ); cout<<"count=" <<myprint.count<<endl; } void doPrint (Myprint myprint,int num) myprint (num); } void test03 () doPrint (Myprint (),555 ); } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
2.谓词
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;class Mycompare { public : bool operator () (int val) { return val > 20 ; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v1; v1.push_back (10 ); v1.push_back (20 ); v1.push_back (30 ); v1.push_back (40 ); Mycompare mycompare; vector<int >::iterator pos=find_if (v1.begin (), v1.end (),mycompare); if (pos != v1.end ()) { cout << "position_nums=" << *pos << endl; } else { cout<< "can't find" << endl; } } class Mycompare1 { public : bool operator () (const int val1,const int val2) const { return val1>val2; } }; void test02 () vector<int > v1; v1.push_back (10 ); v1.push_back (20 ); v1.push_back (30 ); v1.push_back (40 ); Mycompare1 mycompare; sort (v1.begin (),v1.end (),mycompare); for (vector<int >::iterator it=v1.begin ();it!=v1.end ();it++){ cout<<*it<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } int main () test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
3.内建函数对象的使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <functional> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> void PrintVector (vector<int > v) for (vector<int >::iterator it = v.begin (); it != v.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } cout << endl; } void test01 () negate<int > n; cout << "n取反值为=" << n (10 ) << endl; plus<int > p; cout << "加法值为=" << p (2 , 3 ) << endl; vector<int > v; v.push_back (10 ); v.push_back (50 ); v.push_back (60 ); v.push_back (20 ); sort (v.begin (), v.end (), greater <int >()); PrintVector (v); } int main () test01 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
4.适配器的使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> class Myprint : public binary_function<int , int , void > { public : void operator () (int val, int num) const { cout << "val+num=" << val + num << endl; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v1; v1.push_back (10 ); v1.push_back (30 ); v1.push_back (50 ); v1.push_back (40 ); cout << "请输入值:" ; int num; cin >> num; for_each(v1.begin (), v1.end (), bind2nd (Myprint (), num)); } class Myprint2 : public unary_function<int , bool > { public : bool operator () (int val) const { return val > 20 ; } }; void test02 () vector<int > v1; v1.push_back (10 ); v1.push_back (30 ); v1.push_back (50 ); v1.push_back (40 ); vector<int >::iterator pos = find_if (v1.begin (), v1.end (), not1 (Myprint2 ())); cout << *pos << endl; } void Myprint03 (int v, int start) cout << v + start << endl; } void test03 () vector<int > v1; v1.push_back (10 ); v1.push_back (30 ); v1.push_back (50 ); v1.push_back (40 ); for_each(v1.begin (), v1.end (), bind2nd (ptr_fun (Myprint03), 100 )); } class Person { public : int m_Age; string m_Name; Person (string name, int age) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } void showPerson () cout<<"成员函数的姓名:" <<m_Name<<" 年龄:" <<m_Age<<endl; } }; void test04 () Person p1 ("zx" , 18 ) ; Person p2 ("cbl" , 18 ) ; Person p3 ("cjl" , 19 ) ; Person p4 ("hjj" , 20 ) ; Person p5 ("cwq" , 20 ) ; vector<Person> v; v.push_back (p1); v.push_back (p2); v.push_back (p3); v.push_back (p4); v.push_back (p5); for_each(v.begin (),v.end (),mem_fun_ref (&Person::showPerson)); } int main () test04 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
5.常用遍历算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <functional> class Mycompare { public : void operator () (int v) { cout << v << endl; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare ()); } class Mycompare2 { public : void operator () (int v) { cout << v << " " ; count++; } int count = 0 ; }; void test02 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } Mycompare2 mycompare2 = for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare2 ()); cout << endl; cout << "mycount=" << mycompare2.count << endl; } class Mycompare3 : public binary_function<int , int , void >{ public : void operator () (int v, int start) const { cout << v + start << " " ; } }; void test03 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), bind2nd (Mycompare3 (), 100 )); } class TransForm { public : int operator () (int val) { return val + 10 ; } }; void test04 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } vector<int > vTarget; vTarget.resize (v.size ()); transform (v.begin (),v.end (),vTarget.begin (),TransForm ()); for_each(vTarget.begin (),vTarget.end (),Mycompare ()); } class TransForm2 { public : int operator () (int val,int val2) { return val + val2; } }; void test05 () vector<int > v; vector<int > v1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (200 +i); v1.push_back (i+100 ); } vector<int > vTarget; vTarget.resize (v.size ()); transform (v.begin (),v.end (),v1.begin (),vTarget.begin (),TransForm2 ()); for_each(vTarget.begin (),vTarget.end (),Mycompare ()); } int main () test05 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
6.常用查找算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;#include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } vector<int >::iterator pos = find (v.begin (), v.end (), 5 ); if (pos != v.end ()) { cout << "position=" << pos - v.begin () << endl; } else { cout << "Not find" << endl; } } class Person { public : int m_Age; string m_Name; bool operator ==(const Person &p){ if (p.m_Age==this ->m_Age && p.m_Name==this ->m_Name){ return true ; } else { return false ; } } Person (string name, int age) { this ->m_Age = age; this ->m_Name = name; } }; void test02 () vector<Person> v1; Person p1 ("zx" ,18 ) ; Person p2 ("zwh" , 18 ) ; Person p3 ("cbl" , 18 ) ; v1.push_back (p1); v1.push_back (p2); v1.push_back (p3); vector<Person>::iterator pos = find (v1.begin (), v1.end (),p3); if (pos != v1.end ()) { cout << "position=" << pos - v1.begin () << endl; } else { cout << "Not find" << endl; } } class Mycompare :public binary_function<Person *,Person *,bool >{ public : bool operator () (Person *p1, Person *p2) const if (p1->m_Name==p2->m_Name && p1->m_Age==p2->m_Age){ return true ; } else { return false ; } } }; void test03 () vector<Person *> v1; Person p1 ("zx" ,18 ) ; Person p2 ("zwh" , 18 ) ; Person p3 ("cbl" , 18 ) ; v1.push_back (&p1); v1.push_back (&p2); v1.push_back (&p3); Person *p4=new Person ("cbl" , 18 ); vector<Person *>::iterator pos = find_if (v1.begin (), v1.end (),bind2nd (Mycompare (),p4)); if (pos!= v1.end ()) { cout <<"name=" <<(*pos)->m_Name<<" age=" << (*pos)->m_Age<< endl; } else { cout << "Not find" << endl; } } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
7.常用排序算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> using namespace std;class Mycompare { public : void operator () (int v) { cout << v << " " ; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v; vector<int > v1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); v1.push_back (11 + i); } vector<int > vTarget; vTarget.resize (v.size () + v1.size ()); merge (v1.begin (), v1.end (), v.begin (), v.end (), vTarget.begin ()); for_each(vTarget.begin (), vTarget.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; } void test02 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } sort (v.begin (),v.end ()); for_each(v.begin (),v.end (),Mycompare ()); cout<<endl; sort (v.begin (),v.end (),greater <int >()); for_each(v.begin (),v.end (),Mycompare ()); cout<<endl; } void test03 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } random_shuffle (v.begin (),v.end ()); for_each(v.begin (),v.end (),Mycompare ()); cout<<endl; } void test04 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } reverse (v.begin (),v.end ()); for_each(v.begin (),v.end (),Mycompare ()); cout<<endl; } int main () test04 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
8.常见拷贝和替换算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <functional> using namespace std;class Mycompare { public : void operator () (int v) { cout << v << " " ; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } vector<int > vTarget; vTarget.resize (v.size ()); copy (v.begin (),v.end (),vTarget.begin ()); for_each(vTarget.begin (), vTarget.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; } class Myreplace { public : bool operator () (int val) return val>3 ; } }; void test02 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } replace (v.begin (),v.end (),3 ,15 ); for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; replace_if (v.begin (),v.end (),Myreplace (),15 ); for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; } void test03 () vector<int > v; vector<int > v1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); v1.push_back (100 +i); } swap (v,v1); for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; for_each(v1.begin (), v1.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; } int main () test03 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
9.常用算数生成算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <numeric> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;class Mycompare { public : void operator () (int v) { cout << v << " " ; } }; void test01 () vector<int > v; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 100 ; i++) { v.push_back (i); } cout << "sum=" << accumulate (v.begin (), v.end (), 0 ) << endl; } void test02 () vector<int > v; v.resize (10 ); fill (v.begin (), v.end (), 100 ); for_each(v.begin (), v.end (), Mycompare ()); cout << endl; } int main () test01 (); test02 (); system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
10.常用集合算法
11.STL综合案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 #include <iostream> using namespace std;#include "string" #include <vector> #include <list> #include "set" #include <algorithm> #include "functional" #include "iterator" #include <numeric> #include "map" #include "deque" class Speaker { public : string m_name; int m_score[3 ]; }; int GenSpeaker (map<int , Speaker> &mapSpeaker, vector<int > &v) string str = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" ; random_shuffle (str.begin (), str.end ()); for (int i = 0 ; i < 24 ; i++) { Speaker tmp; tmp.m_name = "选手" ; tmp.m_name = tmp.m_name + str[i]; mapSpeaker.insert (pair <int , Speaker>(100 + i, tmp)); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 24 ; i++) { v.push_back (100 + i); } return 0 ; } int speech_contest_draw (vector<int > &v) random_shuffle (v.begin (), v.end ()); return 0 ; } int speech_contest (int index, vector<int > &v1, map<int , Speaker> &mapSpeaker, vector<int > &v2) multimap<int , int , greater<int >> multmapGroup; int tmpCount = 0 ; for (vector<int >::iterator it = v1.begin (); it != v1.end (); it++) { tmpCount++; { deque<int > dscore; for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++) { int score = 50 + rand () % 50 ; dscore.push_back (score); } sort (dscore.begin (), dscore.end ()); dscore.pop_back (); dscore.pop_front (); int scoresum = accumulate (dscore.begin (), dscore.end (), 0 ); int scoreavg = scoresum / dscore.size (); mapSpeaker[*it].m_score[index] = scoreavg; multmapGroup.insert (pair <int , int >(scoreavg, *it)); } if (tmpCount % 6 == 0 ) { cout << "小组的比赛成绩" << endl; for (multimap<int , int , greater<int >>::iterator mit = multmapGroup.begin (); mit != multmapGroup.end (); mit++) { cout << mit->second << "\t" << mapSpeaker[mit->second].m_name << "\t" << mit->first << endl; } while (multmapGroup.size () > 3 ) { multimap<int , int , greater<int >>::iterator it1 = multmapGroup.begin (); v2.push_back (it1->second); multmapGroup.erase (it1); } multmapGroup.clear (); } } return 0 ; }; int speech_contest_print (int index, vector<int > &v, map<int , Speaker> &mapSpeaker) printf ("第%d轮 晋级名单\n" , index + 1 ); for (vector<int >::iterator it = v.begin (); it != v.end (); it++) { cout << "参赛编号: " << *it << "\t" << mapSpeaker[*it].m_name << "\t" << mapSpeaker[*it].m_score[index] << endl; } return 0 ; }; int main () map<int , Speaker> mapSpeaker; vector<int > v1; vector<int > v2; vector<int > v3; vector<int > v4; GenSpeaker (mapSpeaker, v1); cout << "\n\n\n任意键,开始第1轮比赛" << endl; cin.get (); speech_contest_draw (v1); speech_contest (0 , v1, mapSpeaker, v2); speech_contest_print (0 , v2, mapSpeaker); cout << "\n\n\n任意键,开始第2轮比赛" << endl; cin.get (); speech_contest_draw (v2); speech_contest (1 , v2, mapSpeaker, v3); speech_contest_print (1 , v3, mapSpeaker); cout << "\n\n\n任意键,开始第3轮比赛" << endl; cin.get (); speech_contest_draw (v3); speech_contest (2 , v3, mapSpeaker, v4); speech_contest_print (2 , v4, mapSpeaker); cout << "hello..." << endl; system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
补充知识点 1.空指针的值输出
2.指针的比较 指针比较的是地址大小,一般例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int MAX = 3 ; int main () int var[MAX] = {10 , 100 , 200 }; int *ptr; ptr = var; int i = 0 ; while ( ptr <= &var[MAX - 1 ] ) { cout << "Address of var[" << i << "] = " ; cout << ptr << endl; cout << "Value of var[" << i << "] = " ; cout << *ptr << endl; ptr++; i++; } return 0 ; }
这个就是比较的例子,ptr<= &var[MAX - 1]就是来判断地址是否超过数组的边界。
3.指针和数组的互换,注意事项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int MAX = 3 ;int main () int var[MAX] = {10 , 100 , 200 }; cout << *var << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) { *var = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) { cout << var[i] << endl; } system ("pause" ); return 0 ; }
数组不想指针 var++是不对的。
4.指针数组 指针数组跟数组其实差别不大,就是赋值的时候是把别的数组对应地址赋值给它。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int MAX = 3 ; int main () int var[MAX] = {10 , 100 , 200 }; int *ptr[MAX]; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) { ptr[i] = &var[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) { cout << "Value of var[" << i << "] = " ; cout << *ptr[i] << endl; } return 0 ; }
5.C++ 传递指针给函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 void swap (int *p1,int *p2) int temp=*p1; *p1=*p2; *p2=temp; }
6.指针常量和常量指针
7.const关键字 https://www.cnblogs.com/Forever-Kenlen-Ja/p/3776991.html